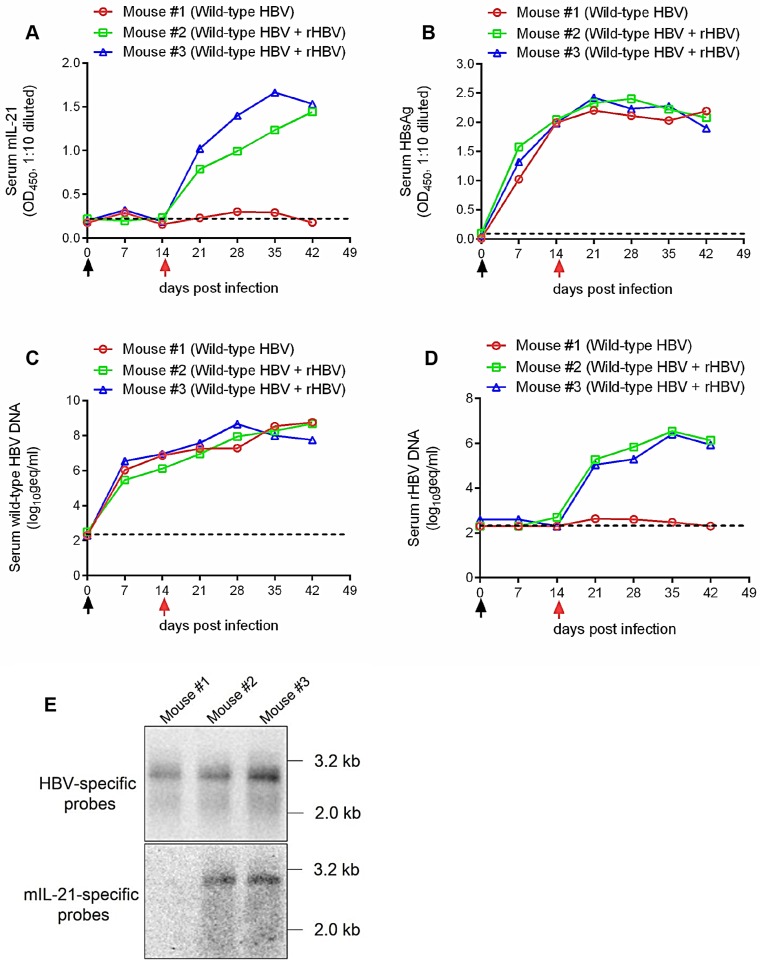
Figure 6.
Superinfection of HBV-infected human hepatocytes in human liver chimeric mice by mIL-21-expressing rHBV. Human liver chimeric mice were first infected with wild type HBV by injection using concentrated sera from pCMV1.1HBV injected mice (black arrows) via tail vein. At 14 days post infection (d.p.i.), mice were injected with concentrated sea from 5c3c-mIL-21/pLMS co-injected mice (red arrows), or left untreated. Sera were collected at indicated time points. Serum mIL-21 (A) and HBsAg (B) were analyzed using ELISA. Serum wild type HBV DNA (C) and rHBV DNA (D) at indicated time points were assayed using quantitative real time PCR. At 42 d.p.i., intrahepatic wild-type HBV and rHBV replication were analyzed in Southern blot using HBV- and mIL-21-specific probes, respectively (E). Dotted lines represent cut-off thresholds (A and B) and lower limit of quantification (C and D), respectively. geq, genome equivalents.