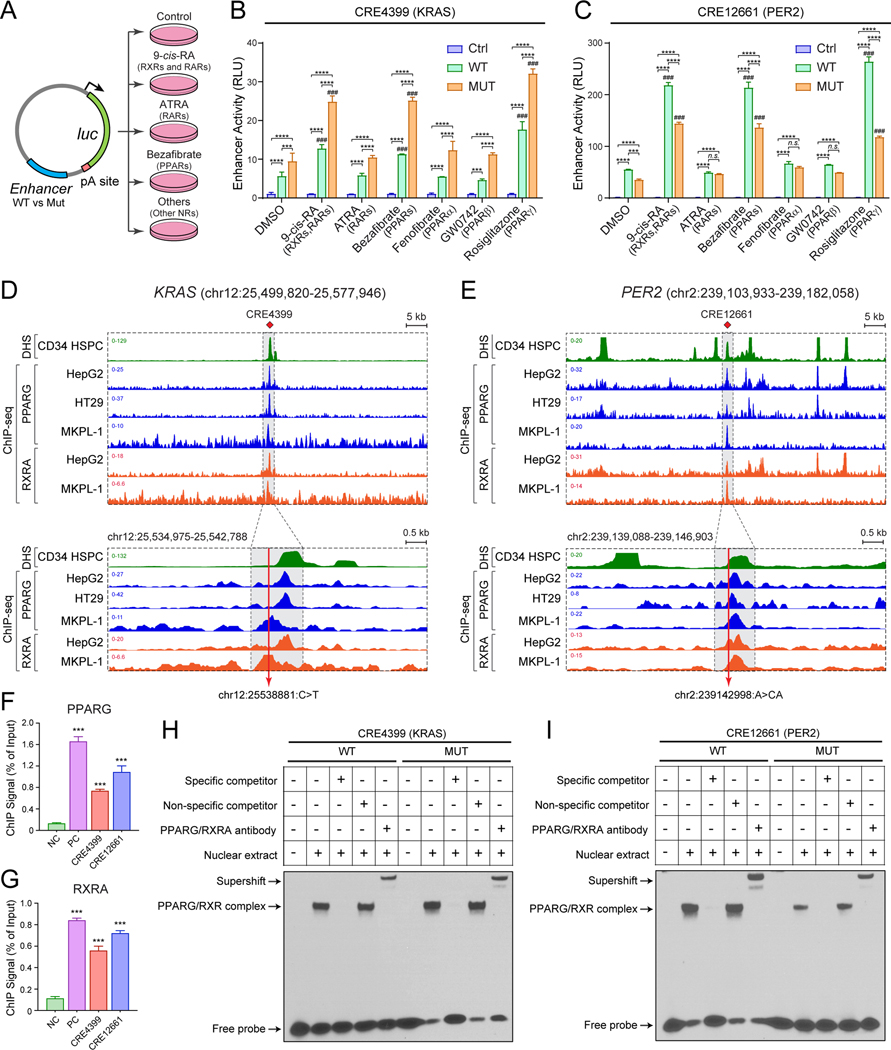
Figure 5. Non-coding variants modify nuclear receptor signaling in leukemia.
(A) Schematic of enhancer reporter assays with or without agonists for nuclear receptors.
(B) KRAS (CRE4399) enhancer variant significantly increased enhancer activity upon activation of RXR and PPARG signaling in MKPL-1 cells. Results are mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. The differences between control (Ctrl) and WT or MUT enhancer were analyzed by a two-way ANOVA with Turkey correction for multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. The differences between DMSO and NR agonist-treated groups were analyzed by a two-way ANOVA with Turkey correction for multiple comparisons. ###P < 0.001.
(C) PER2 (CRE12661) enhancer variant significantly decreased enhancer activity upon activation of RXR and PPARG signaling in MKPL-1 cells. Results are mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments and analyzed by a two-way ANOVA.
(D) RXRA and PPARG strongly associate with the KRAS enhancer in various cell types including MKPL-1 AML cells by ChIP-seq analysis. The annotated KRAS enhancer (CRE4399) is shown as shaded lines. The zoom-in view is also shown in which the AML-associated enhancer variant is indicated by the red line.
(E) RXRA and PPARG strongly associate with the PER2 enhancer in various cell types including MKPL-1 cells. The annotated PER2 enhancer (CRE12661) is shown as shaded lines and the AML-associated enhancer variant is indicated by the red line.
(F) Validation of PPARG binding to KRAS and PER2 enhancers by ChIP-qPCR analysis. The ChIP signal (% of input) is shown for the negative control (NC; chr2:211,337,339–211,337,429; hg19) genomic region, the positive control (PC; chr17:41,400,528–41,400,677; hg19), and KRAS (CRE4399) and PER2 (CRE12661) enhancers. Results are mean ± SEM (N = 4 replicate experiments) and analyzed by a one-way ANOVA. ***P < 0.001.
(G) Validation of RXRA binding to KRAS and PER2 enhancers by ChIP-qPCR analysis. Results are mean ± SEM (N = 4 replicate experiments) and analyzed by a one-way ANOVA. ***P < 0.001.
(H) Non-coding variant at the KRAS enhancer increased PPARG and RXRA binding. EMSA was performed using MKPL-1 nuclear extracts co-transduced with PPARG and RXRA expressing lentiviruses. Excess unlabeled PPARG/RXRA-binding probe, but not non-specific competitor, abolished the gel shift with both WT and MUT CRE4399 probes. PPARG and RXRA antibodies supershifted protein-DNA complexes. A representative image from 3 independent experiments is shown. The quantification of binding intensity is shown in Fig. S11K.
(I) Non-coding variant at the PER2 enhancer impaired PPARG and RXRA binding. The quantification is shown in Fig. S11K.