Table 2.
Clinically significant natural product based molecules in attenuating respiratory disorders.
| Alkaloids | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr. No | Compound | Source | Structure | Application | Mechanism | Ref. |
| 1. | Theophylline | Camellia sinensis and Theobroma cacao | 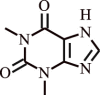 |
Inhibits the Exacerbations in human subjects with COPD, bronchodilation | Suppression of inflammatory genes by enhanced HDAC activation | [121,122] |
| 2. | Ligustrazine | Ligusticum wallichii Rhizome, Curcuma aromatica Salisb, Jatropha podagrica Hook | 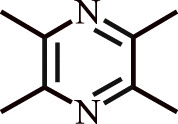 |
Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in human subjects | Upregulates levels of NO and downregulates ET-1; lowers mPAP levels. |
[123,124] |
| 3. | Atropine | Family Solanaceae | 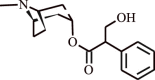 |
Relieves asthma chronic bronchitis | Reduction in sputum volume | [125] |
| Flavonoids | ||||||
| 4. | Puerarin | Pueraria montana var. lobata | 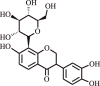 |
Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in human subjects | Restrains pulmonary vascular remodeling | [126] |
| Procyanidin | Cocoa | 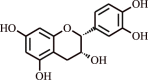 |
Relieves oxidant stress in human subjects | Trigger Nrf2 activity | [127] | |
| Terpenoids | ||||||
| 5. | Carvacrol | Origanum vulgare | 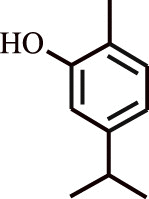 |
Therapeutic effect on asthma in human subjects | Downregulation of inflammatory cells, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) | [128] |
| 6. | Eukalyptol | Eucalyptus sp. | 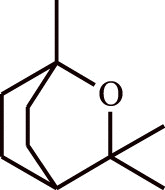 |
Relieves bronchial asthma and rhinosinusitis in human subjects | Mucolytic agent in upper and lower airway passages | [129,130] |
| 7. | Boswellic acid | Boswellia serrata | 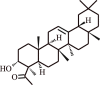 |
Alleviates symptoms of asthma in human subjects | Deactivation of lipoxygenase pathway | [131] |
| Miscellaneous | ||||||
| 8. | Sulforaphane | cruciferous vegetables |  |
Attenuates inflammatory effects of oxidative stress in respiratory passages in human subjects | Induces the expression of mucosal Phase II enzymes in the upper airway passage | [132] |
| 9 | Curcumin | Zingiberaceaefamily | 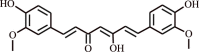 |
Prevention of deleterious cardiovascular events in COPD human subjects | Decreased the atherosclerotic AT-LDL levels, resulting in prevention of possible cardiovascular disorders in COPD subjects | [133] |
| 10 | Pycnogenol | Pinus pinaster | Complex antioxidant compounds | Relieves asthma inflammation in human subjects | Inactivation of NF-κB and attenuation of MMP-9 secretion | [134] |
| 11 | Linoleic acid | Vegetable oils | Polyunsaturated fatty acid | Improves the airway hyper‐reactivity in asthma human subjects | Downregulation of stimulated TNF-α | [[135], [136], [137]] |
| 12 | Caffeic acid | Eucalyptus globulus | 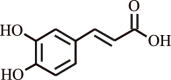 |
Significant inhibition in the incidence and severity of nocturnal attacks, improvement of ventilatory functions in asthma human subjects | Reduction in pro‐inflammatory factors (TNF)‐α, ICAM‐1, IL‐6, IL‐8, prostaglandins E2 and F2α and leukotriene D4; upsurge in IL‐10. The levels of | [138] |
