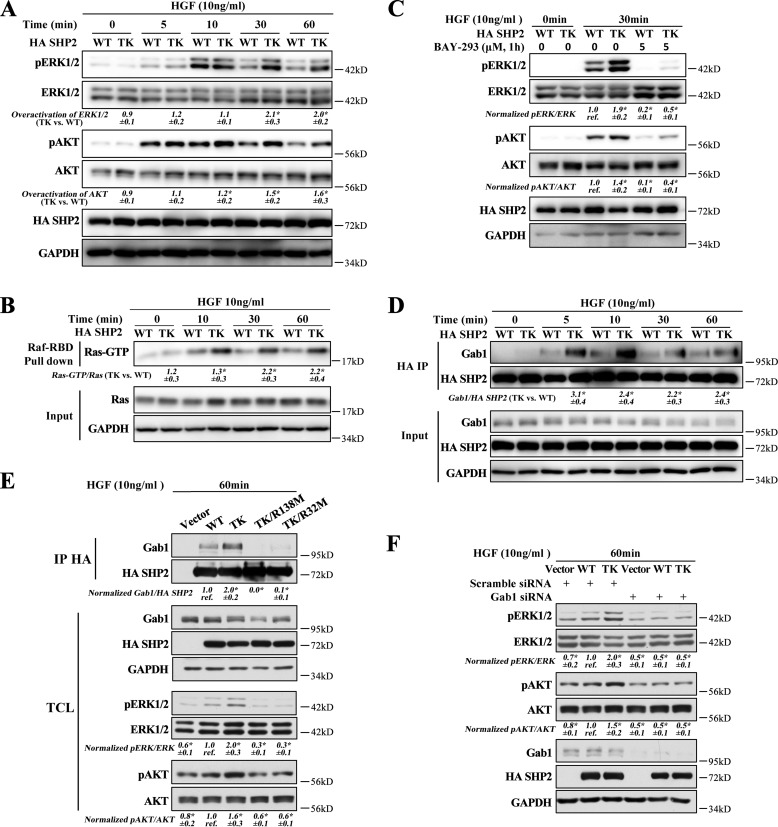
Figure 5.
SHP2/T507K preferentially binds with Gab1 and overactivates Ras, ERK1/2, and AKT. A, compared with WT SHP2, the T507K mutant can further activate ERK1/2 and AKT upon HGF stimulation at later time points (i.e. 30 and 60 min). The overactivation of ERK1/2 by the SHP2/T507K mutant was defined as SHP2/T507K-induced ERK1/2 activation (i.e. pERK1/2/ERK1/2 in SHP2/T507K-expressing cells) over WT SHP2-induced ERK1/2 activation (i.e. pERK1/2/ERK1/2 in WT SHP2-expressing cells). The overactivation of AKT was calculated the same way but using the ratio pAKT/AKT. B, SHP2/T507K mutant promotes Ras activation at later time points versus WT SHP2. C, Ras–SOS binding inhibitor BAY-293 blocks ERK1/2 and AKT activation in WT SHP2 and the T507K mutant cells. D, SHP2/T507K preferentially binds and stays longer with Gab1 upon HGF stimulation. E, mutation of Arg-32 or Arg-138 to Met in SHP2/T507K abolishes its binding with Gab1 and significantly suppresses HGF-induced ERK1/2 and AKT activation. F, Gab1 knockdown impairs the ERK1/2 or AKT activation in both WT SHP2- and SHP2/T507K-overexpressed cells and eliminates the excessive ERK1/2 or AKT activation for SHP2/T507K. The results of Western blottings are representative of three independent experiments, and the star in the figure indicates statistical significance from Student's t test (p < 0.05). IP, immunoprecipitation; TCL means total-cell lysate; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.