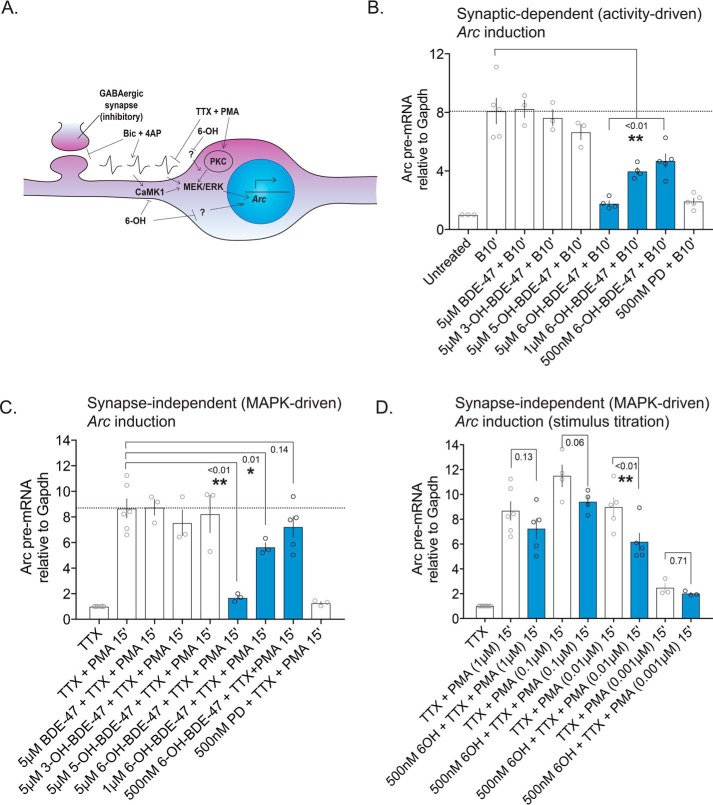
Figure 5.
Acute 6-OH–BDE-47 exposure attenuates activity and MEK–ERK-dependent Arc transcription. MAPK-dependent gene transcription was evaluated as a measure of 6-OH–mediated MEK–ERK inhibition by quantifying levels of Arc pre-mRNA following multiple stimulation approaches. A, graphical depiction of the stimulation methods used: Bic + 4AP synaptically activates MEK–ERK signaling via depolarization, whereas TTX + PMA suppresses neuronal activity and activates MEK membrane-independently via PKC. Both ultimately drive induction of Arc gene transcription. B, Arc pre-mRNA levels were estimated following exposure to BDE-47 or one of its hydroxylated metabolites, and treatment with Bic (50 μm) and 4AP (75 μm), n = 3–5, p values generated by one-way ANOVA with post hoc LSD. Treatment F(7,24) = 25.1, p < 0.0001. C, similar to B, except that cells were stimulated with TTX (1 μm)) and PMA (1 μm)), n = 3–6. Treatment F(7,21) = 12.14, p < 0.0001. D, assessment of the effect of stimulus strength on inhibition of Arc induction by 6-OH. Neurons were acutely exposed to 500 nm 6-OH before stimulus with a range of PMA concentrations (1 μm)-1 nm), n = 3–6. p values generated by two-way ANOVA with post hoc LSD. PMA-dose: F(3,27) = 33.16, p < 0.0001; 6-OH exposure: F(1,27) = 9.969, p = 0.0039; interaction: F(3,27) = 0.7964, p = 0.5066.