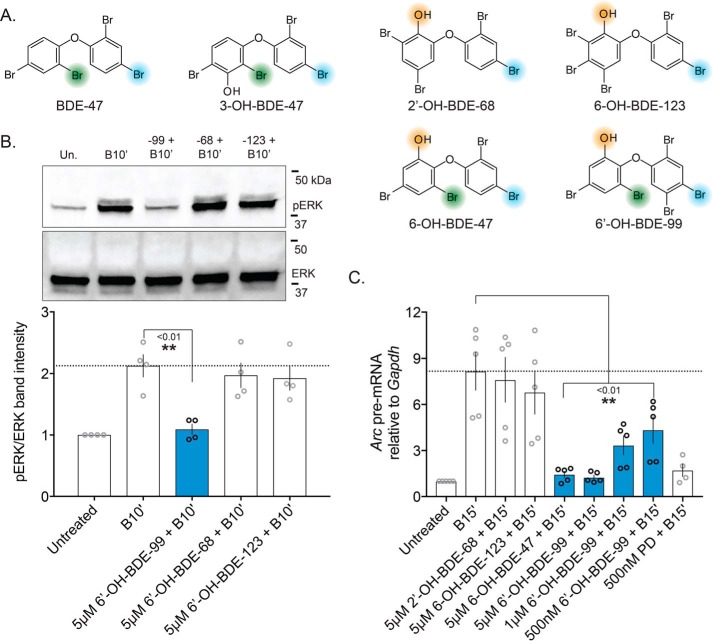
Figure 6.
Specific ortho-hydroxylated PBDE metabolites impair neuronal MEK–ERK signaling. In an effort to generalize our hypothesis that ortho-hydroxylated PBDE metabolites can inhibit MEK–ERK signaling, both approaches used to evaluate MEK inhibition by BDE-47 and its metabolites (Figs. 4 and 5) were re-employed with several additional ortho-hydroxylated metabolites. A, chemical structures of PBDEs screened, with key substituents for potential MEK1 binding highlighted, specifically indicating the newly-identified ortho-halogen thought to be critical for inhibition of MEK–ERK signaling. B, representative Western blotting measuring pERK levels after exposure to various ortho-hydroxylated PBDEs (top) with quantification of blots summarized (bottom), n = 4. p values were generated by one-way ANOVA with post hoc LSD. Treatment: F(3,12) = 7.314, p = 0.0048. C, similar PBDE metabolite exposures as in B, but evaluating Arc pre-mRNA level attenuation by BDE-47 and BDE-99 metabolites, n = 4–5. Treatment: F(7,31) = 8.837, p < 0.0001.