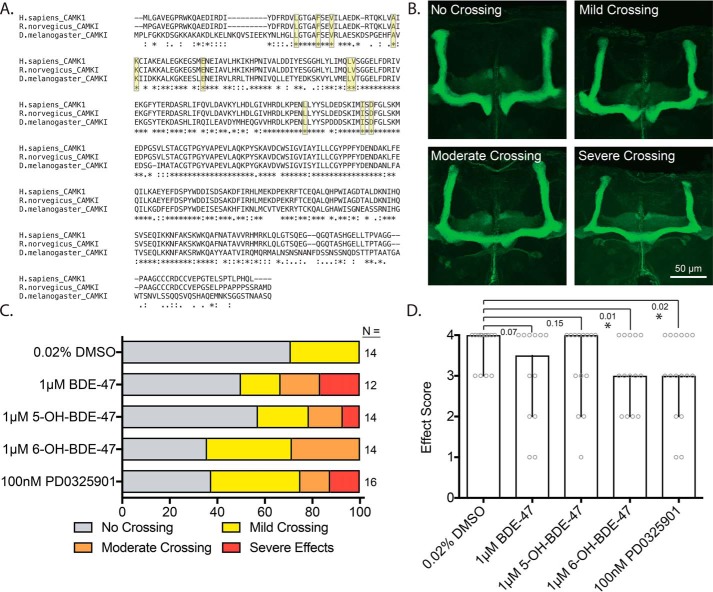
Figure 7.
In vivo exposure to 6-OH–BDE-47 and the MEK inhibitor PD0325901 disrupt axonal guidance. Canton-S flies (D. melanogaster) were exposed to BDE-47, 5-OH, 6-OH, or PD via feeding. The mushroom bodies of offspring were then assessed for aberrant midline crossing. A, alignment of the amino acid sequences of human CaMK1 and its rat and fly orthologs. The proteins are highly conserved, including the key residues thought to mediate ATP-competitive inhibitor binding (highlighted in yellow). B, example images of the effect categories used in the qualitative scoring scheme. C, crossing frequency by severity level for each of the treatment groups, n = 12–16. D, crossing severity was numerically ranked scored as follows. No crossing, 4; mild crossing, 3; moderate crossing, 2; severe crossing and/or lobe malformation, 1. Bars represent the median score of each treatment group that was generated from the values of the crossing data from C, after application of the numerical scoring scheme (the score for each fly is additionally plotted as gray circles). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. p values were generated using exact one-tailed Mann-Whitney tests to compare the median of each group with that of the DMSO control, n = 12–16.