Figure 2. The conserved ABCE1‐30S interface is formed by essential interactions.
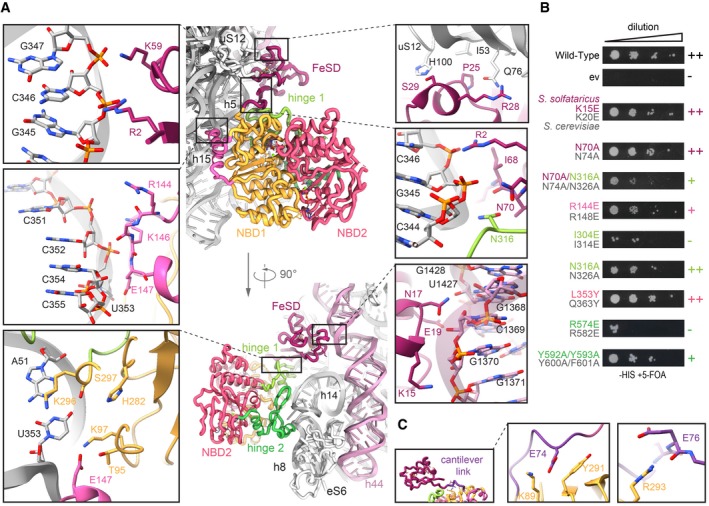
- Zoom‐ins into ABCE1‐30S connections. Most interactions are salt bridges or H‐bonds between ABCE1 residues and the rRNA phosphate backbone. The FeSD cluster domain contacts rRNA h5 via R2 and K59, interacts with uS12 via S29 and R28, and contacts h44 by N17 and K15. The helix‐loop‐helix motif connects to rRNA h15 via R144 and E147. The positioning of the cantilever is stabilized by an interaction network of R2, I68, and N70 with N316 of hinge 1 and rRNA h5.
- Yeast survival of ABCE1 variants (S. solfataricus colored, S. cerevisiae in gray). Most residues connecting to 30S in the post‐SC show a growth defect when exchanged for a small one (alanine) or a negative charge (glutamate). ++ no effect, + growth defect, − lethal.
- The cantilever link forms salt bridges of E74 and E76 with NBD1 residues K89 and R293, respectively.
