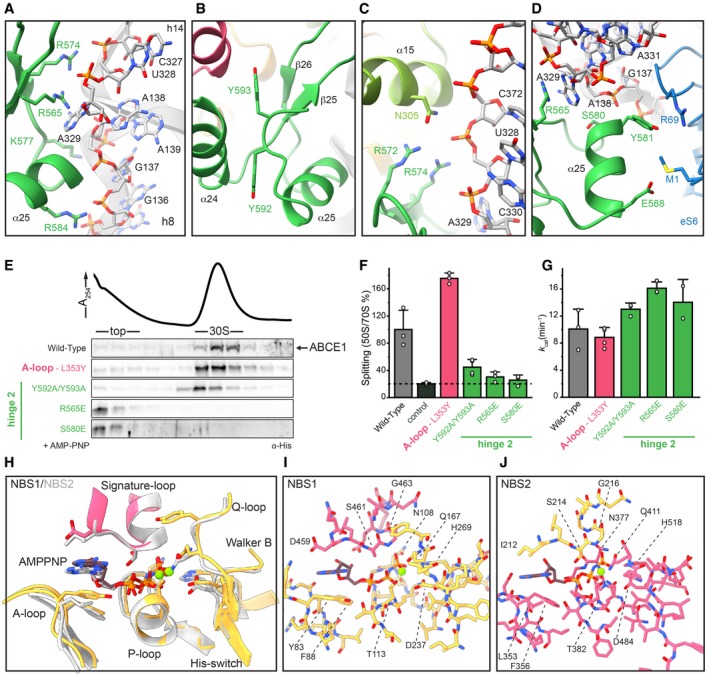
Figure 3. Structural and functional analysis of the hinge regions and NBSs.
-
A–DHinge 2 (emerald) residues interacting with the ribosome. R565E forms a conserved cation‐π‐stacking with A329 of h8; R574 forms a salt bridge with the phosphate backbone of U328 in h14. Aromatic C‐terminal residues Y592 and Y593 adopt a parallel coordination. R572 of hinge 2 and N305 of hinge 1 (light green) form an interaction that might be important for sensing. Essential S580 does not contact the ribosome, whereas Y581 and E588 form H‐bonds to R69 and M1 of eS6 (blue), respectively.
-
EMutations in the α‐helices of hinge 2 prevent 30S binding while the Y592A/Y593A (C terminus) and L353Y (A‐loop in NBSII) exchanges do not influence ribosome binding.
-
F70S splitting efficiency normalized to wild type. Hinge 2 mutations Y592A/Y593A, R565E, and S580E display strongly impaired splitting activity. Unspecific ribosome dissociation level as determined in control experiments in the absence of ABCE1 is marked by the dotted line.
-
GATP turnover per ABCE1 is not affected in all tested mutants.
-
H–JOverview of ATP coordination in both NBSs and overlay of the two NBSs reveals only slight differences, which cannot elucidate the functional asymmetry. Residues of NBD1 and NBD2 involved in coordination are shown in gold and punch, respectively.
