Figure 2.
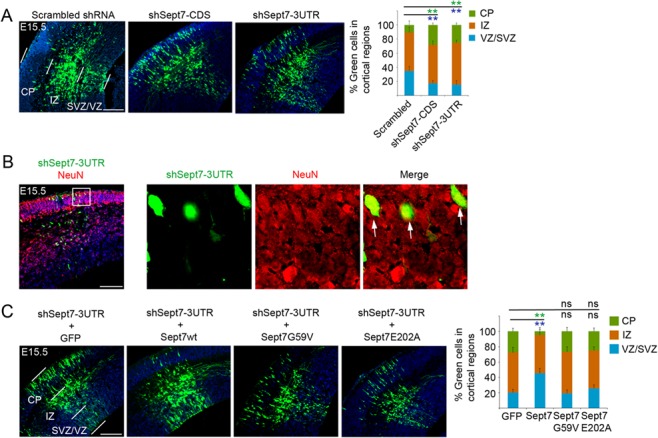
Knockdown of SEPT7 causes neuronal differentiation of NPCs. (A) shRNA-expressing plasmids were introduced into the cortex by IUE at E13.5 and the brains were analyzed at E15.5. The shRNA vector carried an ubiquitin promoter-GFP expression cassette for visualization of transfected cells. Distributions of transfected cells in different radial regions of the cortex were scored (6–9 electroporated brains for each plasmid were used for quantification). ** (in green and blue font) indicated P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test) with respect to the CP and VZ/SVZ distributions compared with control shRNA. Scale bar represents 100 μm. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD). SVZ, subventricular zone. (B) Two days after IUE, shSept7-expressing cells (GFP+ cells) in the CP were positive for NeuN, indicating that these cells were neuronal progeny. Arrows indicated examples of GFP+NeuN+ cells. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (C) shRNA-expressing plasmid and expression plasmid for GFP or different Sept7 proteins were cointroduced into the cortex by IUE at E13.5 and the brains were analyzed at E15.5. Distributions of transfected cells in different radial regions of the cortex were scored. Wild-type Sept7 protein could rescue the inhibition by shSept7-3UTR, but the two mutant Sept7 proteins did not. ** (in green and blue font) indicated P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test) with respect to the CP and VZ/SVZ distributions compared with the control. ns, not significant (P > 0.05). Scale bar represents 100 μm.
