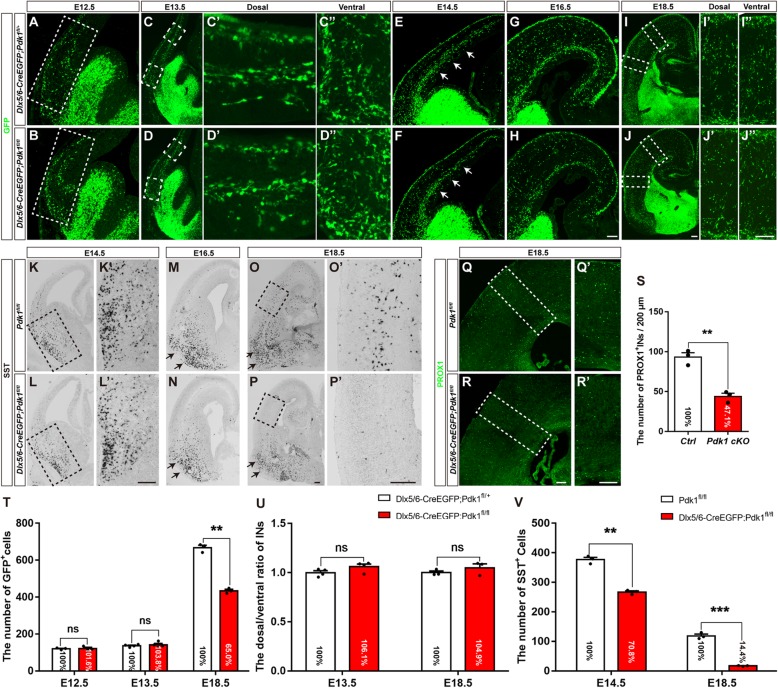
Fig. 2.
Embryonic loss of cortical interneurons with unchanged tangential migration after Pdk1 deletion. (a-d”) Immunofluorescence for GFP in coronal sections showed comparable distribution patterns and numbers of cortical interneurons at E12.5 and E13.5 between Pdk1 cKO and control mice. (e-f) Immunofluorescence for GFP revealed that the number of GFP+ cortical interneurons in the SVZ was reduced in the Pdk1 cKO cortex at E14.5. (g-j”) The number of GFP+ cortical interneurons in the Pdk1 cKO cortex gradually decreased from E16.5 to E18.5. (t) Statistical analysis of GFP+ interneurons (E12.5 Ctrl: N = 3, Pdk1 cKO: N = 3, P = 0.9912; E13.5 Ctrl: N = 4, Pdk1 cKO: N = 4, P = 0.9089; E18.5 Ctrl: N = 3, Pdk1 cKO: N = 3, P = 0.00034, Multiple t-test, with alpha = 0.05/3 = 0.0167). (u) Statistical analysis the dorsal/ventral ratio of the numbers of GFP+ interneurons between Pdk1 cKO and control mice at E13.5 and E18.5 (E13.5 Ctrl: N = 4, Pdk1 cKO: N = 4, P = 0.1945; E18.5 Ctrl: N = 3, Pdk1 cKO: N = 3, P = 0.5371, Multiple t-test, with alpha = 0.05/2 = 0.025). (k-n) In situ hybridization showed that the number of SST+ interneurons in the Pdk1 cKO subpallium gradually decreased from E14.5 to E16.5. (o-p′) The number of SST+ interneurons in the Pdk1 cKO cortex was decreased at E18.5. (V) Statistical analysis of SST+ interneurons (E14.5 Ctrl: N = 3, Pdk1 cKO: N = 3, P = 0.00045; E18.5 Ctrl: N = 3, Pdk1 cKO: N = 3, P = 0.00016, Multiple t-test, with alpha = 0.05/2 = 0.025). (q-r’) Immunofluorescence for PROX1 showed that the number of PROX1+ cortical interneurons was decreased in the Pdk1 cKO cortex at E18.5. (s) Statistical analysis of PROX1+ interneurons (Ctrl: N = 3; Pdk1 cKO: N = 3; P = 0.0018, Student’s t-test, with alpha = 0.05). The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Scale bar, 100 μm