Figure 3.
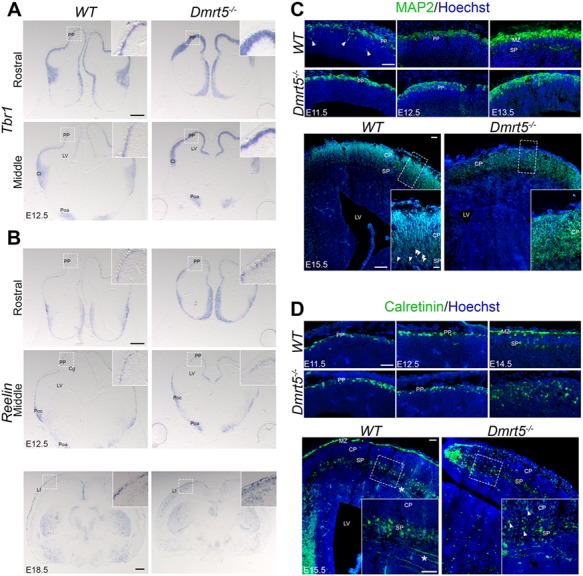
Early SP development and subsequent cortical neuron migration are affected in Dmrt5 mutants. (A, B) ISH for (A) Tbr1 and (B) Reelin in coronal sections from WT and Dmrt5−/− embryos at E12.5 (and E18.5 for Reelin). Tbr1 and Reelin have a comparable distribution in PP, Cl, and Poc; Poa and Cg in WT and Dmrt5−/− embryos at E12.5. Note that Tbr1 is overexpressed in Dmrt5−/− embryos (A). Note that while Cajal-Retzius and PP neurons are detectable in the cortex of both WT and Dmrt5−/− embryos at E12.5, Reelin expression is decreased at E18.5 in Dmrt5−/− compared with WT brains and fewer Reelin+ cells are located in the MZ (B). In each panel, a high-magnification image of the boxed area is shown. (C, D) Coronal sections of developing brains from WT and Dmrt5−/− embryos from E11.5 to E15.5 were immunostained for MAP2 (C) and Calretinin (D) and counterstained with Hoechst (blue). Views of the lateral cortex at various stages are shown, with high magnification of the boxed area in insets. At E13.5–E15.5, MAP2 is detected in CP and SPn (white arrowheads in high-magnification box of E15.5 WT) in the cortex of WT embryos, whereas no cytoarchitectonically distinct SP can be detected in the cortex of Dmrt5−/− embryos, the majority of the CP neurons showing orientation defects. In WT, Calretinin is expressed in the SP layer and in the MZ. Some of the earliest corticofugal projections are also immunoreactive and extend through the intermediate zone towards the internal capsule in WT and Dmrt5−/− (white asterisk in lower left panel at D). Note that the disorganized band of calretinin positive cells in the SP region of the cortex of Dmrt5−/−embryos, and the presence of ectopic Calretinin+ cells within the CP with abnormal shape (white arrowheads). Clumpings of Calretinin+ cells are observed at the edge of the medial cortex close to Hpc in WT and Dmrt5−/− embryonic brains. Scale bars represent 50 μm for immunofluorescence images and 500 μm for ISH images. Cg: cingulate; CP: cortical plate; LV: lateral ventricle; Poa: preoptic area; Poc: prospective olfactory cortex.
