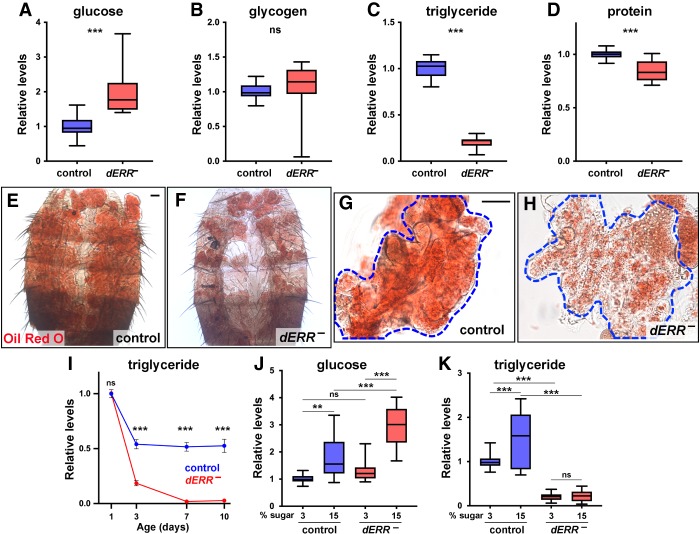
Figure 2.
dERR is required for adult metabolic homeostasis and establishing adult triglyceride stores. (A–D) Whole animal homogenates from controls (blue) and dERR mutants (red) at day 6 of adulthood were analyzed for glucose (A), glycogen (B), triglyceride (C), and protein (D) levels. Data is normalized to the controls. Animals were fed a normal diet; n = 17–23 independent samples with five animals per sample. (E–H) Bright-field images of adult fat bodies from six day-old controls (E,G) and dERR mutants (F,H) stained with Oil Red O to detect neutral lipids. Representative images show the dorsal fat body attached to the abdominal cuticle (E,F), or dissected dorsal fat bodies (G,H). n = 12 animals analyzed. Scale bar, 50 µm. (I) Triglyceride levels were measured from whole animal homogenates of controls (blue) and dERR mutants (red) collected at 1, 3, 7, and 10 d of adulthood. Animals were fed a normal diet and all data is normalized to 1-d control levels. n = 6 independent samples with five animals per sample. Points indicate mean ± SEM. (J,K) Whole animal homogenates from 6-d-old controls (blue) and dERR mutants (red) were analyzed for glucose and triglyceride levels following exposure to a 3% or 15% sugar diet from days 2 to 6 of adulthood. Data were normalized to controls on a 3% sugar diet. n = 18 independent samples with five animals per sample. (***) P ≤ 0.001; (**) P ≤ 0.01; (ns) P > 0.05.