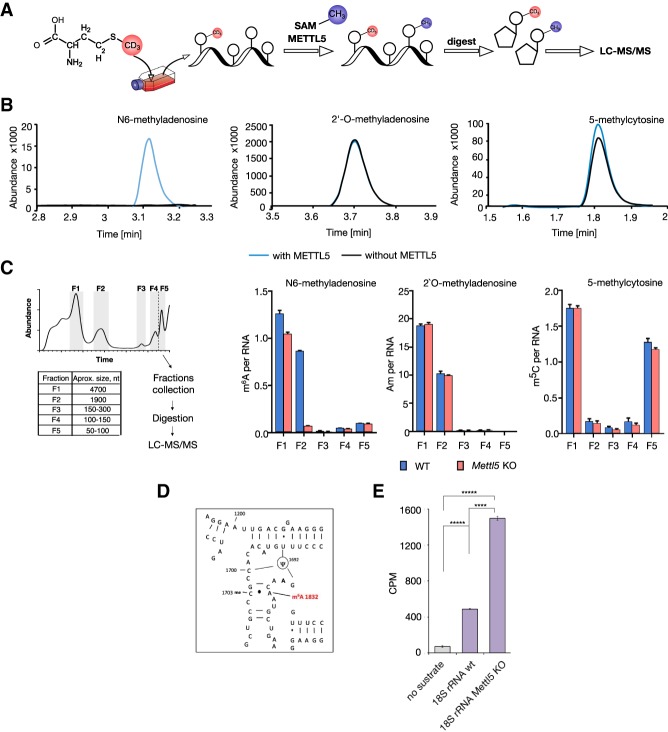
Figure 2.
METTL5 catalyzes m6A formation in RNA in vitro and in cells. (A) Principle of Methyl-NAIL-MS (Nucleic acid isotope labeling-coupled mass spectrometry) (Reichle et al. 2019). Cells were grown in the presence of CD3-methionine for metabolic D3-labeling of methylated nucleosides. Total RNA isolated from these cells was in vitro methylated by recombinant METTL5 with unlabeled SAM. RNA was digested and methylated nucleosides were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. (B) LC-MS/MS elution profiles of indicated modifications in in vitro methylated RNA. In vitro methylated nucleosides (blue) can be distinguished from endogenous methylations (black) by a mass shift of +3 Da. Overlaid MS/MS chromatograms of 6-methyladenosine (m6A), 2′-O-methyladenosine (Am), and 5-methylcytosine (m5C) are shown. (C, left) Scheme of RNA size exclusion chromatography followed by LC-MS/MS (Chionh et al. 2013). The collected and analyzed fractions are highlighted in gray with sizes of the predominant RNA species per fraction (F1: 28S rRNA; F2: 18S rRNA; F3: 5.8S rRNA and 5S rRNA; F4: 5S rRNA; F5: tRNAs and pri-miRNAs) in the table. (Right) Absolute quantifications of modified nucleosides per respective RNA for 6-methyladenosine (m6A), 2′-O-methyladenosine (Am), and 7-methylguanosine (m7G) (Borland et al. 2019). Average of three biological replicates and SD are plotted. See Supplemental Figure S2b for additional data. The small decrease in m6A abundance in fraction F1 could be due to a minor contamination with 18S rRNA as suggested by model from Piekna-Przybylska et al. (2008) (see also https://people.biochem.umass.edu/fournierlab/3dmodmap/humssu2dframes.php). (E) In vitro RNA MTA with recombinant GFP-METTL5 on 18S rRNA isolated from WT and Mettl5 KO mESC with tritium-labeled SAM. Tritium signal was quantified by liquid scintillation counting (LSC). CPMs for one representative experiment as averages of three technical replicates with SD are plotted. (****) P < 0.0001; (*****) P < 0.00001, calculated with Welch's test (unpaired t-test).