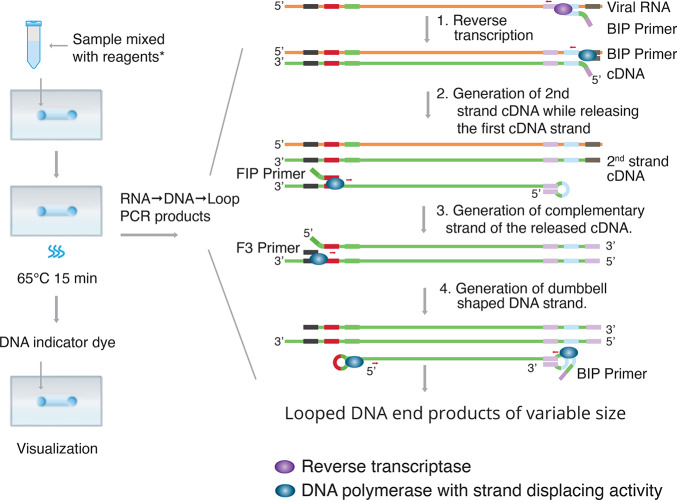
Figure 2.
Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP). Step 1: At the 3′-end of the viral RNA, reverse transcriptase and BIP primer initiate conversion of RNA to cDNA. Step 2: At the same end, DNA polymerase and B3 primer continue to generate the second cDNA strand to displace and release the first cDNA strand. Step 3: The FIP primer binds to the released cDNA strand and DNA polymerase generates the complementary strand. Step 4: F3 primer binds to the 3′ end, and DNA polymerase then generates a new strand while displacing the old strand. LAMP cycling produces various sized double-stranded looped DNA structures containing alternately inverted repeats of the target sequence as detected by a DNA indicator dye. Reagents*: Primers and master mix containing reverse transcriptase, DNA polymerase with strand displacing activity, dNTPs, and buffers.