Figure 3.
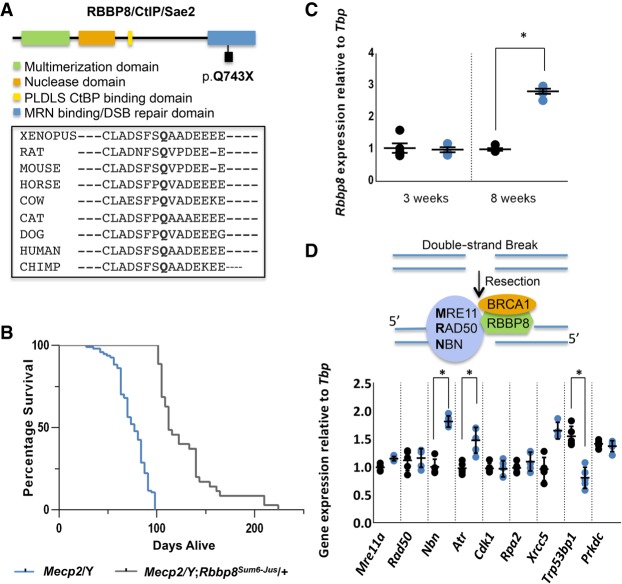
The DNA damage response (DDR) pathway is implicated in a Mecp2/Y mouse model of Rett syndrome. (A) An ENU-induced nonsense mutation occurs at position p.Q743X within the critical C-terminal double-strand break (DSB) repair domain (blue) of RBBP8, also called CtBP interacting protein CtIP or SAE2 in yeast. Amino acid alignments generated using Clustal Omega show that this glutamine residue is well conserved among organisms from Xenopus to human. (B) Mecp2/Y;Rbbp8Sum6-Jus/+ mice (gray) have increased longevity (n = 35, Median survival 112 d) when compared to Mecp2/Y mice (blue) (n = 94, Median survival 77 d) without secondary mutations (P < 0.0001 by Mantel-Cox test). (C) Rbbp8 transcripts are elevated in symptomatic at 8 wk Mecp2/Y (blue) brain compared to +/Y (black), but unchanged at 3 wk. Results are representative of three independent experiments (P < 0.01 by the two-sample Student's t-test, +/Y: n = 5, Mecp2/Y: n = 5); error bars represent SEM. (D) Double-strand break repair by homologous recombination involves the recruitment of RBBP8 to the site of the break in an MRN/BRCA1-dependent manner. RBBP8 partners with BRCA1 to initiate DNA resection. Transcript levels of genes involved in HR, nibrin (Nbn) and ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related (Atr) are elevated at 8 wk in Mecp2/Y (blue) brain, whereas NHEJ gene transformation related protein 53 binding protein 1 (Trp53bp1) is decreased compared to +/Y (black) (P < 0.05 by the two-sample Student's t-test, +/Y: n = 5, Mecp2/Y: n = 5); error bars represent SEM.