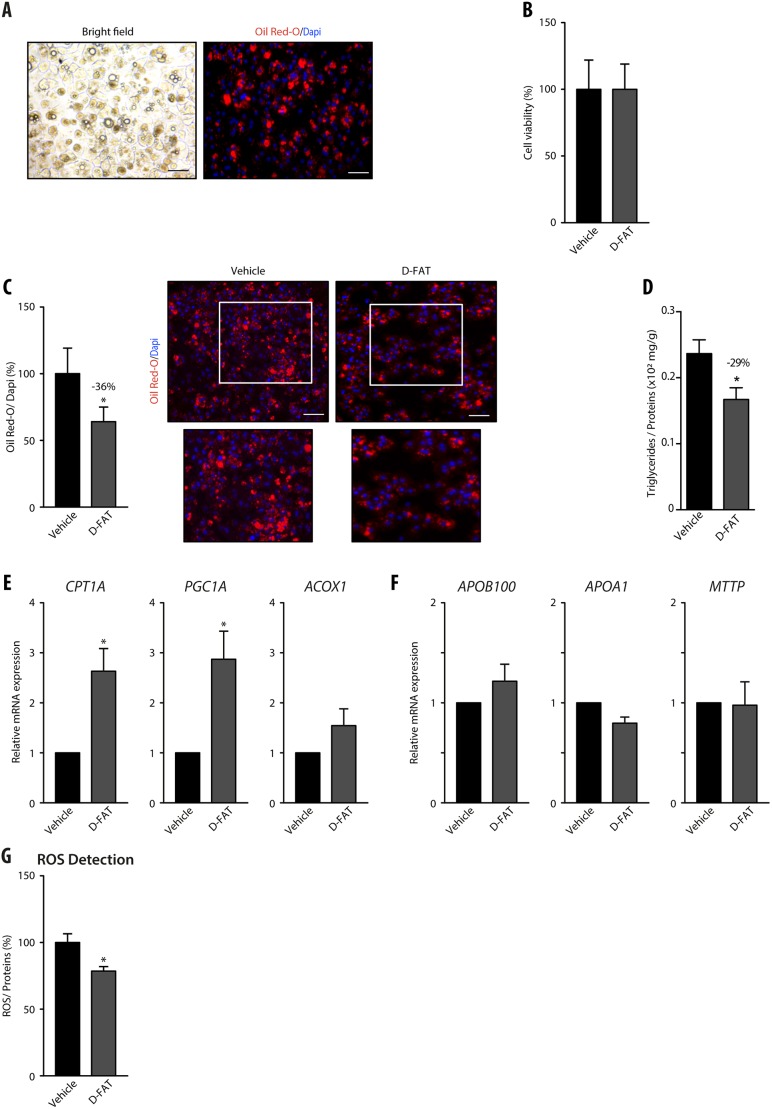
Fig. 3.
Efficacy of the D-FAT cocktail on steatotic hepatocytes isolated from human fatty liver. (A-G) Hepatocytes were isolated from steatotic human liver samples. After 24 h in primary culture their lipid droplet content was assessed by Oil Red O staining (A). Following treatment with the D-FAT cocktail or vehicle for 24 h, samples were examined for: (B) cell viability, assessed by MTT assay; (C) lipid droplet content, assessed by Oil Red O staining – right panels show representative images of vehicle- and D-FAT-treated steatotic hepatocytes (lower panels show magnification of boxed areas in upper panels), left panel shows quantification of Oil Red O staining, normalized to the number of DAPI-stained nuclei; (D) intracellular TG content normalized to cell protein; (E) RT-qPCR analyses of genes associated with fatty acid β-oxidation (CPT1A, PGC1A, ACOX1); (F) RT-qPCR analyses of genes associated with lipid export (ApoB100, ApoA1 and MTTP). (G) Measurement of intracellular ROS. Data are mean±s.e.m. of six cell preparations, shown relative to vehicle. *P<0.05 versus vehicle (two-tailed Student's t-test). Scale bars: 50 µm.