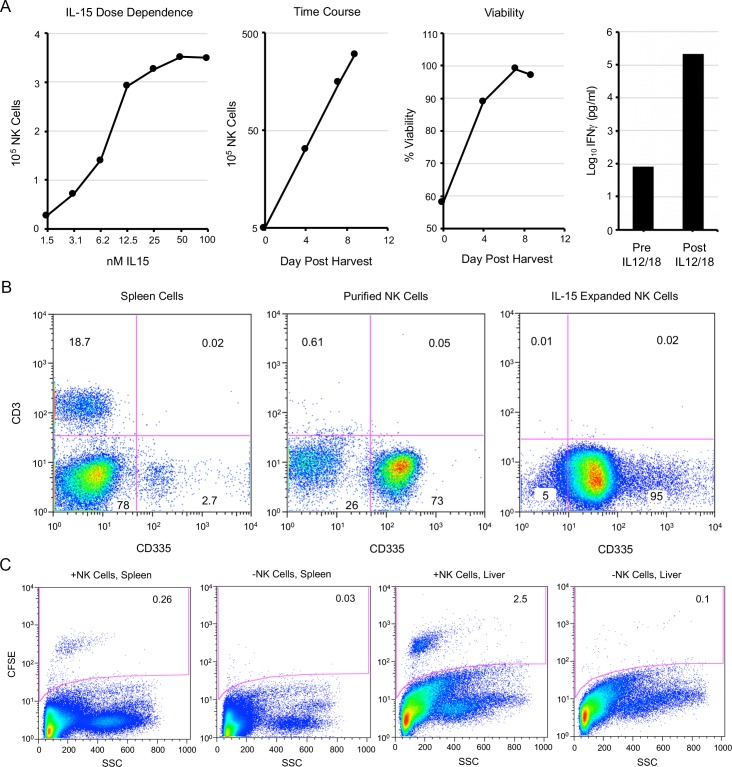
Fig 5. Purification and expansion of splenic NK cells.
(A) Spleen cells from CAST mice were purified by negative selection. In left-most panel, 2-fold dilutions of IL-15 were added to purified NK cells for 5 days at 37°C and counted with a cellometer. Second panel from left shows expansion of NK cells incubated in 50 nM IL-15 over time. Third panel from left shows cell numbers and viability (trypan blue exclusion) determined with a cellometer in presence of 50 nM IL-15. Fourth panel from left shows the amounts of IFN-γ in the medium before and after incubation of expanded NK cells for 18 h with IL-12/IL-18. (B) Spleen cells before and after NK cell purification and following expansion with IL-15 were stained with anti-CD3 and anti-CD335 antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry as described in the legend to Fig 1. (C) Purified and expanded NK cells were stained with CFSE and injected intravenously into CAST mice. After 12 h, spleen and liver cells from the mice injected with NK cells and control mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. Similar findings for CFSE were found in two independent experiments.