Figure 3.
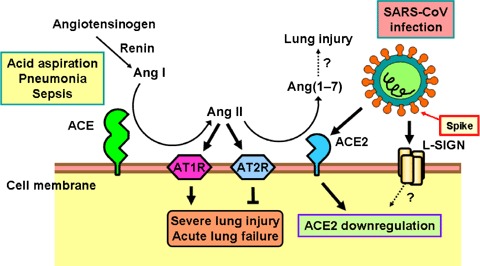
Schematic diagram of the role of the renin–angiotensin system in acute lung failure and proposed SARS‐CoV action In acute lung injury, such as acid aspiration, pneumonia or sepsis, the generation of Ang II from Ang I is enhanced by ACE, and Ang II induces acute lung failure through stimulation of the AT1R, while ACE2 and AT2R negatively regulate this pathway and protect from acute lung failure. In contrast, SARS‐CoV infection is mediated through binding of the SARS Spike protein to ACE2 or liver/lymph node‐specific intercellular adhesion molecule‐3‐grabbing nonintegrin (L‐SIGN) and downregulates the protective molecule ACE2, thus leading to severe lung injury and acute lung failure.
