Fig. 4.
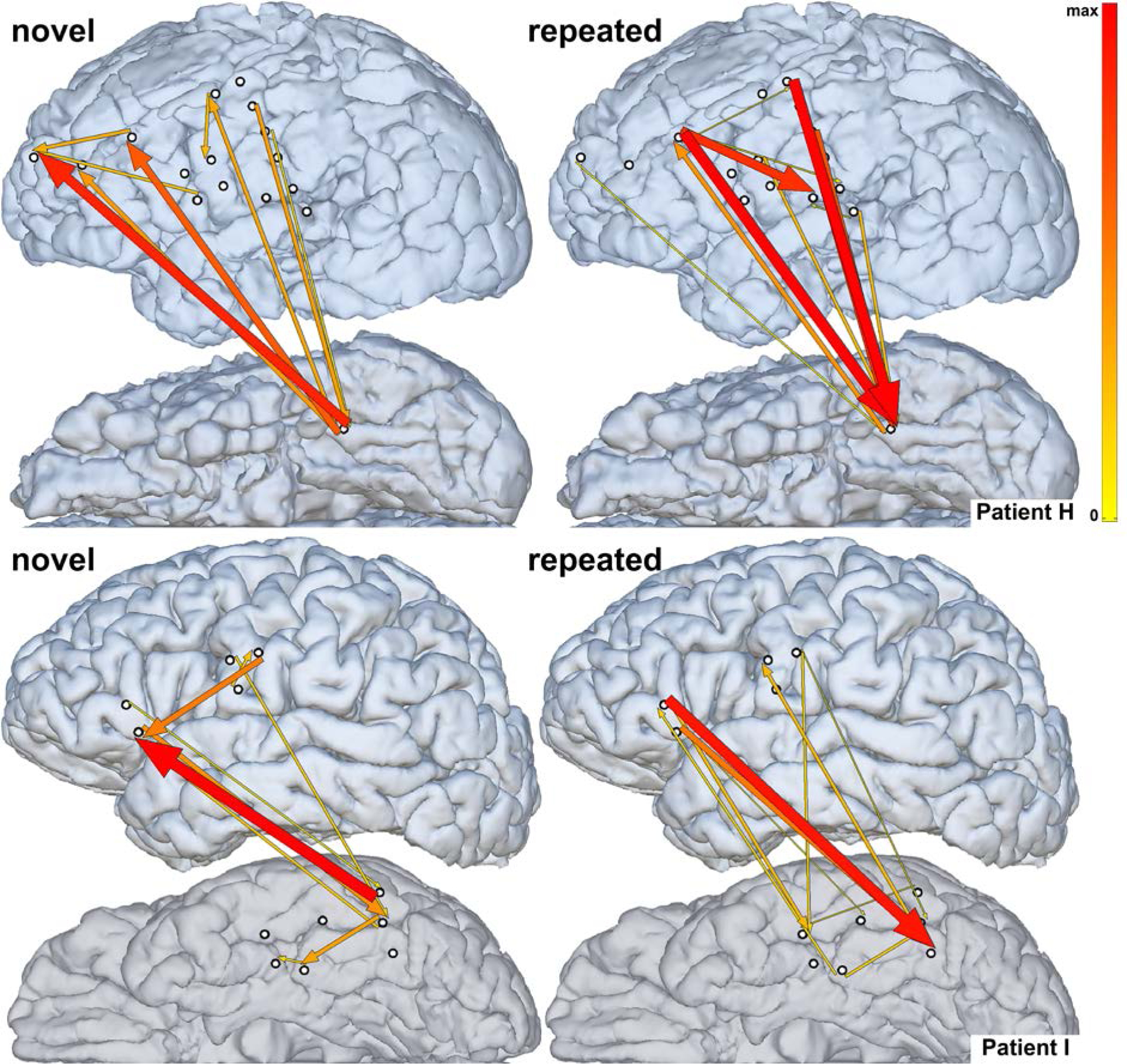
Neural propagation during novel (left) vs. repeated (right) task conditions in two representative patients (top - Patient H, bottom - Patient I) early after stimulus onset (H - 85–450 msec, I - 0–300 msec, taking into account the sliding window length of 140 ms). Arrow width and color both correspond to the strength of estimated ERC flows. Only sites used for estimating ERC flows are shown. Top-down propagation into VOTC is stronger during repeated than during novel task conditions.
