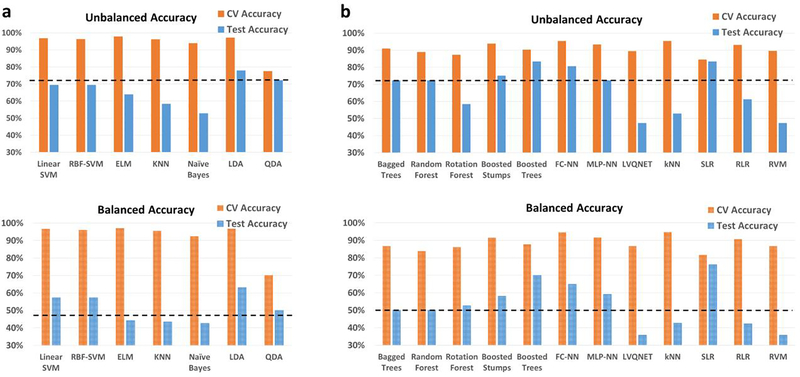
Fig. 6.
Unbalanced and balanced accuracy estimates for various classifiers a within recursive cluster elimination (RCE) framework, b outside RCE framework for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) data when the training/validation data and the hold-out test data are from different age groups in the range for the multiclass classification between healthy controls and subjects with PTSD. The training/validation data is from an age range of 23–37 years while the data from the age range of 38–53 years was used as a hold-out test data. The balanced accuracy was obtained by averaging the individual class accuracies. The orange bars indicate the cross-validation (CV) accuracy while the blue bars indicate the accuracy for the hold-out test data obtained by the voting procedure. The dotted line indicates the accuracy obtained when the classifier assigns the majority class to all subjects in the test data. For unbalanced accuracy, this happens to be 72.2% since subjects with PTSD formed 72.2% of the total size of the hold-out test data. For balanced accuracy, this is exactly 50%. We chose the majority classifier as the benchmark since the accuracy obtained must be greater than that if it learns anything from the training data. The discrepancy between the biased estimates of the CV accuracy and the unbiased estimates of the hold-out accuracy is noteworthy. The best hold-out test accuracy was 83.3% obtained by sparse logistic regression (SLR) and boosted trees, while the best balanced hold-out test accuracy obtained was 76.2% with SLR. ELM, extreme learning machine; KNN, k-nearest neighbors; LDA, linear discriminant analysis; QDA, quadratic discriminant analysis; SVM, support vector machine; FC-NN, fully connected neural network; MLP-NN, multilayer perceptron neural network; LVQNET, learning vector quantization neural network; RLR, regularized logistic regression; RVM, relevance vector machine