Figure 4.
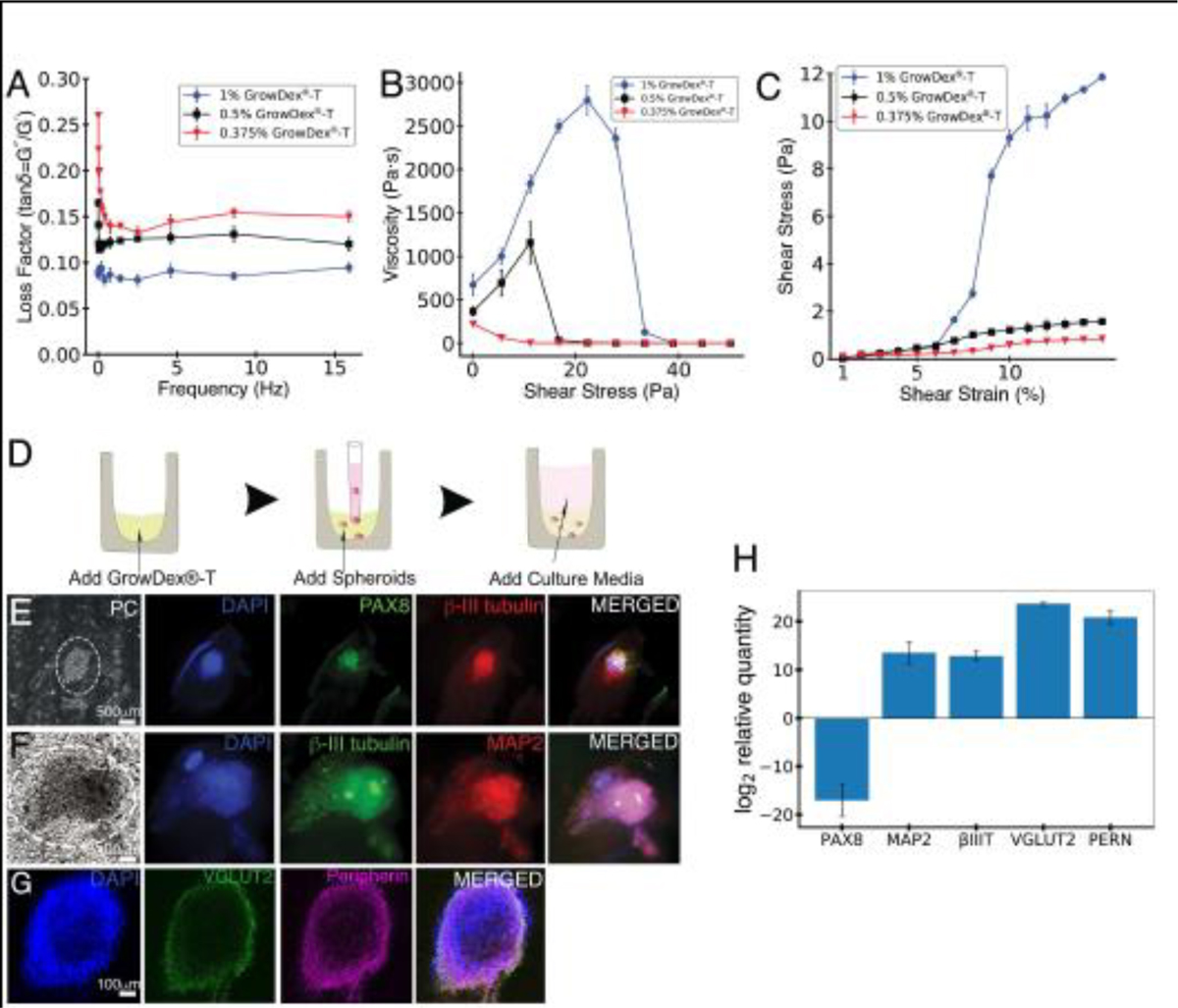
Rheological characterization of GrowDex®-T and hESC-derived ONP spheroids cultured with GrowDex®-T. (A): Frequency sweep (viscoelasticity) of three different concentrations (1%, 0.5%, and 0.375%) of GrowDex®-T (n = 3). (B): Influence of shear stress on the viscosity of three different concentrations (1%, 0.5%, and 0.375%) of GrowDex®-T (n = 3). (C): Strain sweep (stress-strain curve) of three different concentrations (1%, 0.5% and 0.375%) of GrowDex®-T. Shear modulus of 1%, 0.5% and 0.375% GrowDex®-T is plotted as a function of shear strain (n = 3). (D): Schematic figure of hESC-derived ONP spheroids cultured in GrowDex®-T. (E–G): Neuronal marker expressions of PAX8, β-III tubulin, MAP2, VGLUT2, peripherin and phase-contrast of hESC-derived ONP spheroids cultured with 0.375% GrowDex®-T. (H): Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) on hESC-derived ONP spheroids cultured with 0.375% GrowDex®-T and 800,000 of PODS®-hBDNF relative to hESC-derived ONP spheroids cultured in Brainphys™ with 20 ng/mL of recombinant BDNF.
