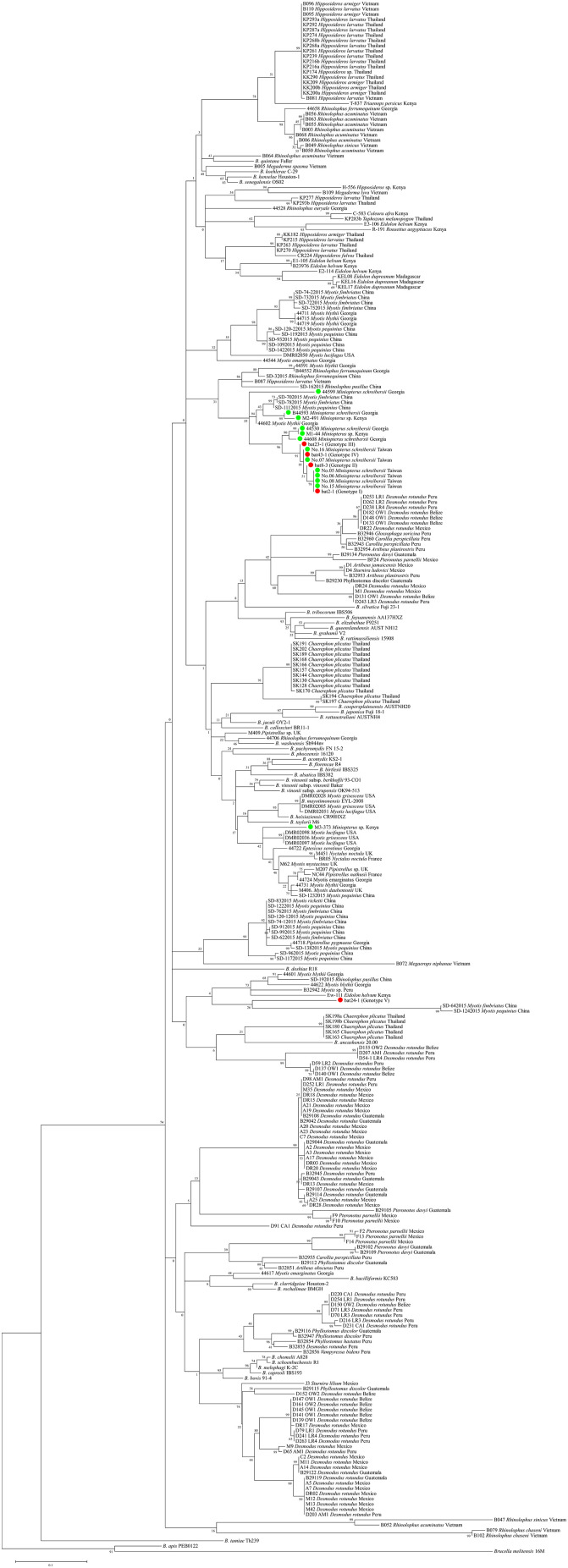
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic relationship of bat-associated Bartonella strains based on the gltA sequences. Evolutionary distances were calculated by Maximum Likelihood method with GTR + G + I model in MEGA 7. The analysis included five representative isolates from M. fuliginosus, 249 bat-associated Bartonella strains, and 41 known type strains of Bartonella species. Bartonella isolates from M. fuliginosus in Japan are indicated by red circles and isolates from Miniopterus bats in Taiwan, Kenya and Georgia are shown by green circles. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)