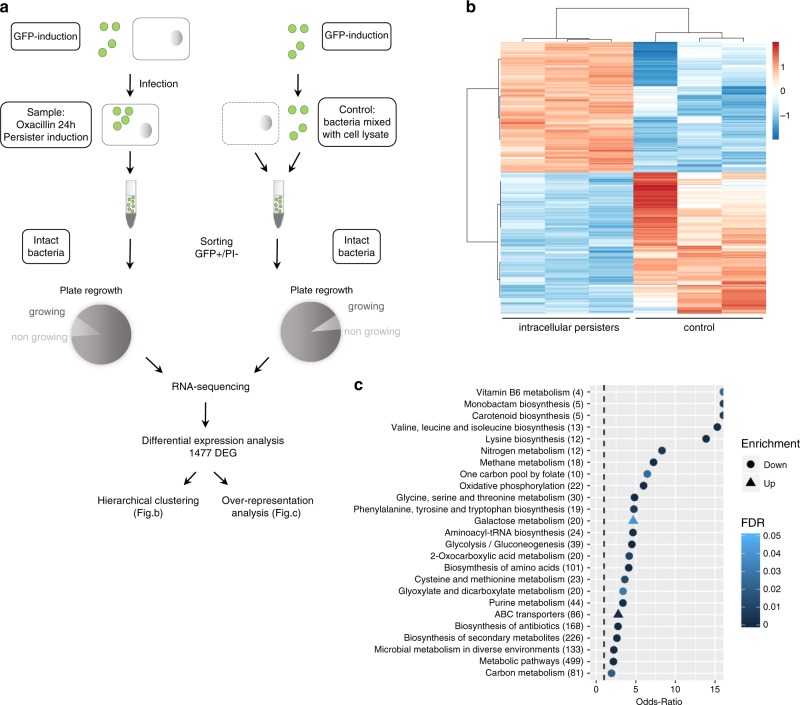
Fig. 2. Intracellular antibiotic-induced persisters exhibit a profoundly altered transcriptomic profile.
a Experimental procedure for sorting and RNA-sequencing of S. aureus persisters of SH1000. Cells infected by GFP-expressing bacteria were exposed to 50x MIC oxacillin to allow for the induction of a homogeneous population of persisters. The subset of intact persisters and control samples were collected and sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) by gating GFP positive (GFP+) and propidium iodide negative signals (PI−), and processed for RNA sequencing (three replicates per condition). 89% and 92% of sorted bacteria from samples and control were able to form colonies, respectively. Differentially expressed genes (DEG) were then analyzed by hierarchical clustering and over-representation analysis. b Heatmap displaying hierarchical clustering of DEGs between intracellular persisters and control samples from three biological replicates (color code is function of a Variance Stabilizing Transformation [VST]). c Over-representation analysis of DEGs. The graph displays over-represented up- and downregulated KEGG gene-sets (EnrichmentBrowser R package), using the Fisher’s Exact Test and evaluated through Odds-Ratio. Only gene-sets with a false discovery rate (FDR) lower than 0.05 were considered significantly enriched. Numbers in brackets represent the number of genes in the gene-set.