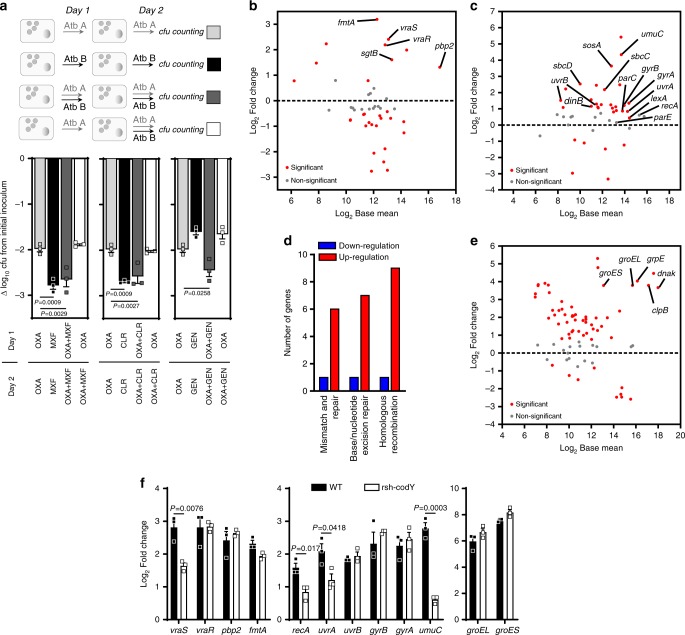
Fig. 5. A mosaic of redundant adaptive responses leads to multidrug tolerance.
a Activity of antibiotic combinations added simultaneously or in succession against intracellular persisters. Intracellular persisters were challenged to 50× MIC of antibiotics alone or in combination, and recovered from macrophages and proceeded for cfu counting after 48 h, following the experimental procedure described above. For combinations, antibiotics were added either at the same time as oxacillin or 24 h after oxacillin. Data (expressed as cfu reduction from the original inoculum) are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test. Oxacillin [OXA], moxifloxacin [MXF], clarithromycin [CLR], gentamicin [GEN]. b, c MA-plots of genes related to peptidoglycan biosynthesis78 (extended to vraS/R and cell-envelope biogenesis genes from the cell wall stress stimulon)80 and SOS response stimulon46,55, respectively. The graphs display the log2 Fold Change expression as a function of log2 Base Mean (mean expression signal across all samples). Typical members of the stimulons are pointed. The dotted lines indicate the basal expression level in control samples. Statistical significance is based on adjusted P-value. d Number of up- or downregulated DEGs related to DNA repair78. e MA-plot of genes related to heat shock stimulon55. f Quantitative real-time PCR of transcripts of determinants of CWSS, SOS response, and heat shock stimulon, from left to right, in HG001 (WT) or HG001 rsh-codY double mutants (Δrsh-ΔcodY) exposed to 50× MIC oxacillin for 2 h of infection. Data are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test. a, f Source data are provided as a Source Data file.