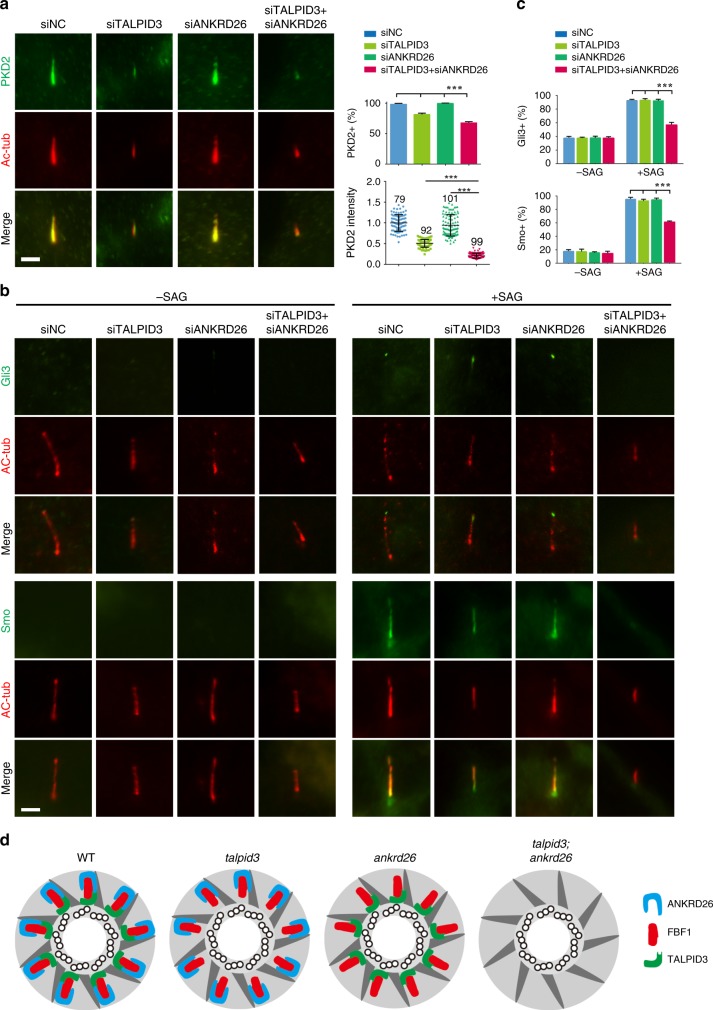
Fig. 7. TALPID3 and ANKRD26 orchestrate the cilia gating for membrane receptors.
The localizations of PKD2 and Shh signaling pathway-associated proteins were analyzed in control, TALPID3 single-knockdown, ANKRD26 single-knockdown and TALPID3 and ANKRD26 double-knockdown RPE cells. Cells were examined by IF staining after 24 h of serum starvation with the indicated antibodies. a Compared with WT, TALPID3 single-knockdown, and ANKRD26 single-knockdown cells, TALPID3 and ANKRD26 double-knockdown cells showed significantly reduced ciliary entry of PKD2. Right panel, both the percentages of cells with PKD2 ciliary signaling and the mean fluorescence intensity in each group were quantified. For PKD2-positive ratio, n = 300 cells over three independent experiments. For PKD2 intensity, numbers of cell examined are indicated above each dataset. b Cells treated without (−SAG) or with (+SAG) SAG were compared to analyze Gli3 and Smoothened (Smo) localization. c The percentages of cells with ciliary Gli3 and Smo were quantified. Results from a minimum of 100 cells in each group were averaged. The results from three independent experiments were statistically analyzed and plotted. n = 300 cells over three independent experiments. d A prospective model of the regulation of FBF1 by TALPID3 and ANKRD26. Recruitment of FBF1 to DAs/TFs or its stabilization on DAs/TFs requires coordination between the distal centriole wall and DA blades. Deletion of TALPID3 compromises the condition of the distal centriole wall, and deletion of ANKRD26 may affect the condition of the DA blade; therefore, co-depletion of TALPID3 and ANKRD26 exacerbates defects in FBF1 localization. All data are presented as the mean ± s.d. Significant differences were identified by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. NS, P > 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. No adjustments were made for multiple comparisons. Scale bars, 2 μm. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.