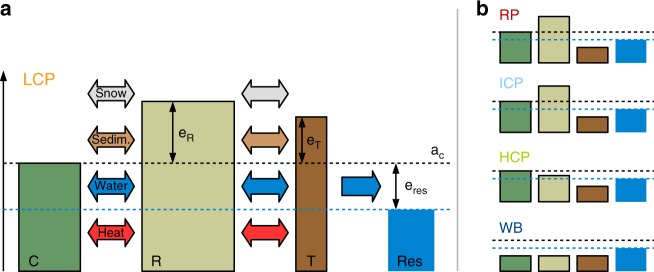
Fig. 5. Schematic of the model set-up.
a Coupled tiles (polygon centres (C), polygon rims (R) and troughs (T)) and an external water reservoir (res) are used to represent surface and subsurface heterogeneities of ice-wedge terrain. The surface microtopography is reflected in different initial elevations (e) relative to the altitude of the centres (aC). Different subsurface stratigraphies are provided in Supplementary Tables 3–5. Lateral fluxes of heat, water, snow and sediment between the tiles were calculated taking into account topological relationships among the tiles (see Supplementary Methods 2 and Supplementary Fig. 10 for details). The parameter eres was used to specify the hydrological conditions. b The microtopographic state of the landscape is defined according to Eqs. (2) to (6) as relict polygons (RP), low-centred polygons (LCP), intermediate-centred polygons (ICP), high-centred polygons (HCP) or water body (WB), depending on the soil surface altitudes of the tiles (aC,R,T) and the elevation of the external water reservoir (eres).