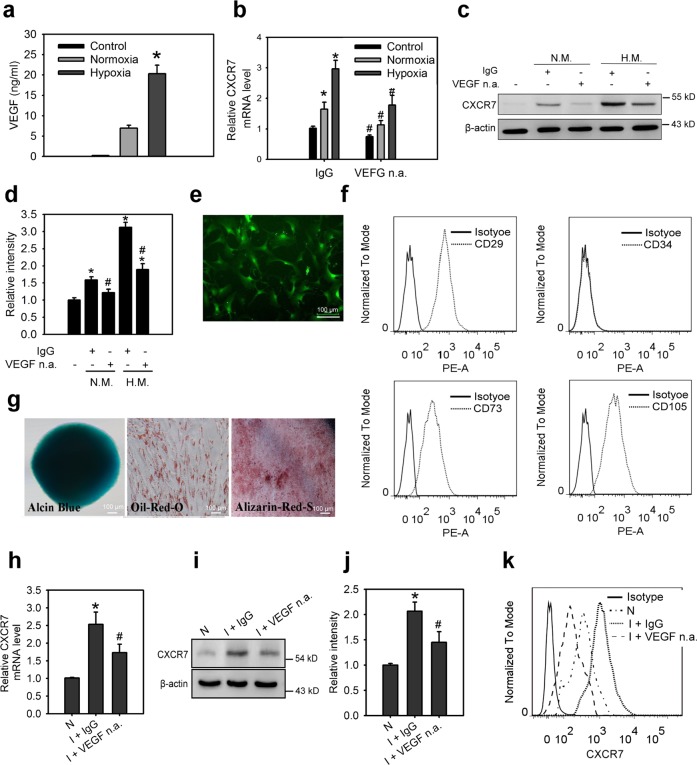
Fig. 1. Skeletal muscle cells-secreted VEGF promotes the upregulation of CXCR7 in MSCs.
a The VEGF concentration in control medium and conditional medium (CM) from SkMC cells incubated in normoxia (N.M.) and hypoxia (H.M.) condition for 24 h. Concentrations of VEGF were examined using ELISA. Data are means ± SD (n = 9). *p < 0.01 compared with the control (untreated) group. The mRNA levels (b), protein levels (c), relative protein densities (d) of CXCR7 in ihMSCs incubated with control medium or CM collected from indicated condition that was treated with or without neutralizing anti-VEGF antibody (VEGF n.a., 100 ng/ml) for 18 h. Data are means ± SD (n = 9). *p < 0.01 compared with the control (untreated) group. #p < 0.01 compared with IgG-treated groups. e The morphology characteristics of mouse GFP+MSCs. f Cell surface co-expression of the antigens CD29, CD34, CD73, and CD105 in mouse GFP+MSCs. g Differentiation potential of mouse GFP+MSCs in osteogenic, chrondrogenic, and adiogenic lineages using Alizarin red, Alcian blue, and Oil red staining, respectively. The mRNA levels (h), protein levels (i), relative protein densities (j), and cell surface expression (k) of CXCR7 in mouse GFP+MSCs isolated from normal lindlimbs (N) or ischemic hindlimbs (I) with neutralizing anti-VEGF antibody or control IgG treatment via a flow sorting of GFP-expressing cells. Animals were treated with VEGF n.a. or control IgG at 10 mg/kg i.p. Hindlimbs were excised for the isolation of mouse GFP+MSCs at 2 days after treatments. Data are means ± SD (n = 9). *p < 0.01 compared with the IgG-treated group.