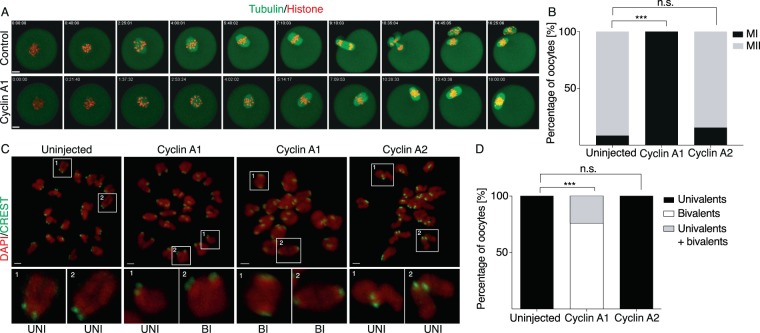
Figure 1.
Expression of cyclin A1 in mouse GV oocytes blocks polar body extrusion and conversion of bivalents into univalent. (A) Frames from live cell imaging experiment of oocytes microinjected with cRNAs encoding tubulin (green) and histone (red) fused to fluorescent proteins, oocyte in lower panel was also co-injected with cRNA encoding cyclin A1. Scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) Scoring of maturation in control – uninjected oocytes (n = 84), oocytes injected with cyclin A1 (n = 44) or cyclin A2 (n = 52) cRNAs. The chart shows percentage of oocytes in meiosis I and meiosis II (control 92% MII; cyclin A1 0% MII; cyclin A2 85% MII) after overnight maturation in each category. The data were obtained in three independent experiments. The difference between control oocytes and oocytes injected with cyclin A1 cRNA was statistically significant (α < 0.05; ***P < 0.0001). The difference between control oocytes and oocytes injected with cyclin A2 cRNA was not statistically significant (α < 0.05; P = 0.2021). (C) Confocal microscopy images showing DNA stained by DAPI (red) and kinetochores stained by CREST antibody (green) in control – uninjected oocytes (left panel), oocytes injected with cyclin A1 cRNA (two central panels) and oocytes injected with cyclin A2. Scale bar represents 2 μm. (D) Scoring of chromosomes status after overnight maturation of control – uninjected oocytes (n = 36), oocytes injected with cyclin A1 cRNA (n = 37) and oocytes injected with cyclin A2 cRNA (n = 43). The percentage of oocytes carrying univalents (control 100%, cyclin A1 0%, cyclin A2 100%), bivalents (control 0%, cyclin A1 76%, cyclin A2 0%) or both (control 0%, cyclin A1 24%, cyclin A2 0%) after overnight meiotic maturation is indicated. The data were obtained in three independent experiments. The difference between control oocytes and oocytes injected with cyclin A1 cRNA was statistically significant (α < 0.05; ***P < 0.0001). The difference between control oocytes and oocytes injected with cyclin A2 cRNA was not statistically significant (α < 0.05; P > 0.9999).