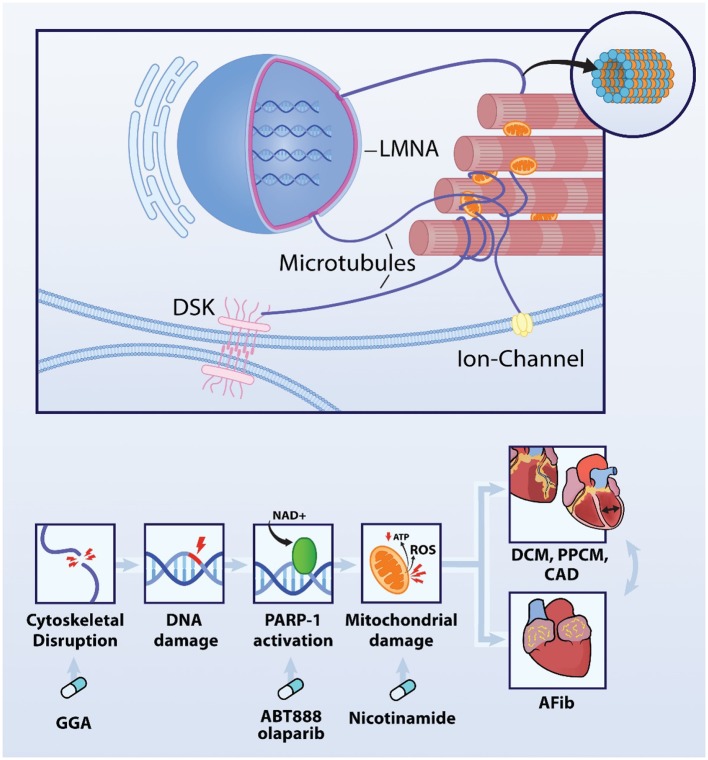
Figure 2.
DNA damage-PARP1-NAD+ axis is involved in AF and additional cardiovascular diseases. AF causes disruption of the microtubule network, DNA damage, PARP1 activation and excessive depletion of the NAD+ levels resulting in ATP depletion and ROS production in the mitochondria. This mechanism is driving AF, Interestingly, comparable mechanism is obverved in LMNA mutation-induced DCM and PPCM as well as atherosclerotic CAD. Importantly, AF is often associated with these cardiovascular diseases, and vice versa indicating that mechanisms driving these cardiac diseases may the enhance each other. Key modulators within this axis are druggable targets as conservation of the cytoskeletal network with the HSP-inducer geranylgeranylacetone (GGA), PARP1 inhibitors ABT-888 and olaparib and precursor of NAD+, nicotinamide protect against AF, CAD, DCM, and PPCM.