FIGURE 6.
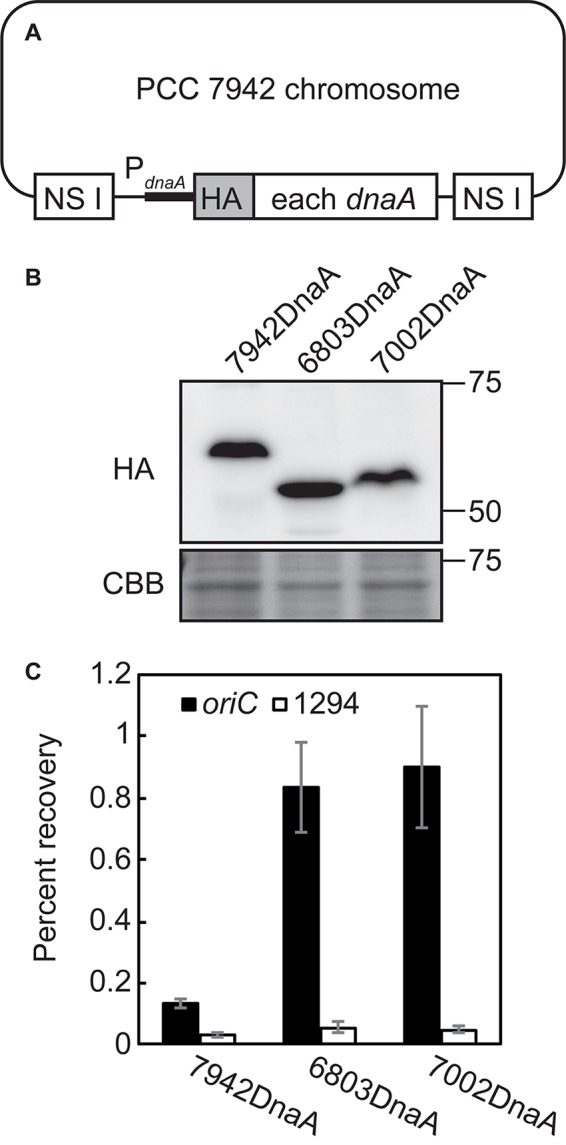
Binding of DnaA to the DnaA-boxes of Synechococcus elongatus, Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, and Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. (A) Diagram of the S. elongatus chromosomes expressing HA-tagged DnaA of S. elongatus (7942 DnaA), Synechocystis (6803 DnaA), and Synechococcus 7002 (7002 DnaA). DNA encoding the respective DnaA was integrated into the chromosomal neutral site I (NS I) of Synechococcus elongatus. HA-DnaA expression was driven by the promoter of S. elongatus dnaA. (B) Immunoblot analysis of the expression of HA-DnaA in S. elongatus. Total proteins were subjected to immunoblotting using an anti-HA antibody. Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB)-stained proteins are shown as a loading control. (C) ChIP-qPCR analysis of the affinity of the binding of DnaA to the oriC region (DnaA-boxes) of the S. elongatus chromosome. The DnaA-chromatin complex was immunoprecipitated using an anti-HA antibody. The samples were quantified using qPCR with the primers representing the oriC region (oriC: solid bar) and Syf1294, which is farthest from oriC in the circular chromosome and lacks a DnaA-box sequence (1294: open bar). The percent recoveries of input DNA are indicated with the standard deviation (n = 3 biological replicates).
