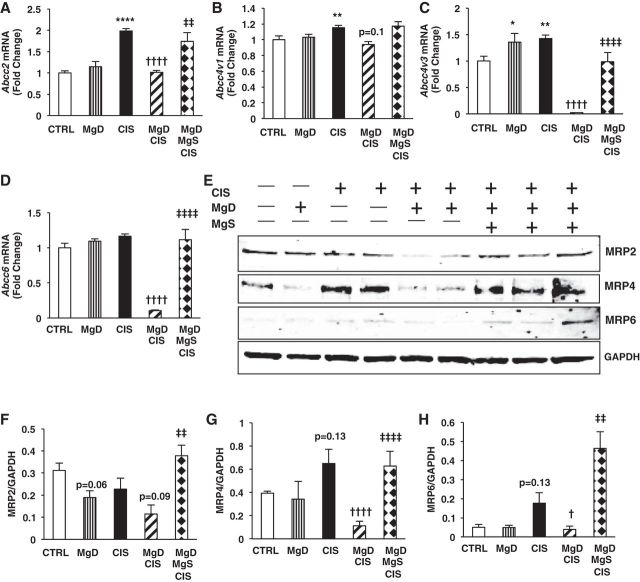
Fig. 11.
Mg status regulates CIS efflux transporter expression in the kidneys. Mice were maintained on either 100% Mg or 10% Mg-deficient diets or were maintained on a 10% Mg diet followed by Mg supplementation, as described in methods, and then treated with saline (CTRL) or CIS (12 mg/kg). All mice were euthanized 48 h post-CIS (or saline), and renal efflux transporter mRNA expression was measured by quantitative PCR. A: ATP-binding cassette subfamily C (ABCC)2. B: Abcc4v1. C: Abcc4v3. D: Abcc6. Data are shown as means ± SE (in fold changes vs. Gapdh). E: representative Western blots for renal ABCC2 [multidrug resistance protein (MRP)2], ABCC6 (MRP6), and ABCC4 (MRP4) expression. F–H: quantitation of band ratios of ABCC2 (MRP2) to GAPDH (F), ABCC4 (MRP4) to GAPDH (G), and ABCC6 (MRP6) to GAPDH (H). Mean band densities ± SE are shown. *P < 0.05 vs. CTRL; **P < 0.01 vs. CTRL; ****P < 0.0001 vs. CTRL; †P < 0.05 vs. CIS; ††††P < 0.0001 vs. CIS; ‡‡P < 0.01 vs. MgD + CIS; ‡‡‡‡P < 0.0001 vs. MgD + CIS; P = 0.06 vs. CTRL; P = 0.13 vs. CTRL; P = 0.09 vs. CIS; P = 0.1 vs. CIS.