FIGURE 1.
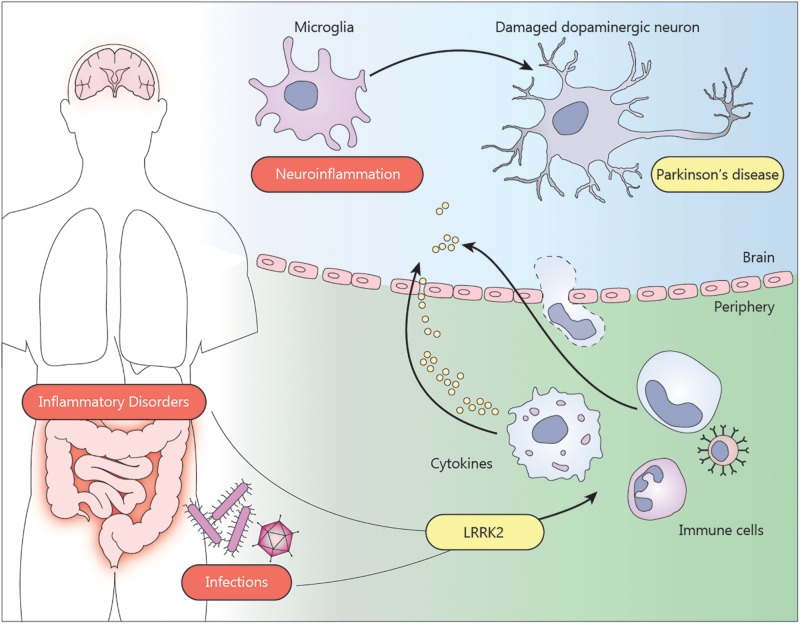
Environmental factors such as inflammatory bowel disease or infections can trigger neuroinflammation and contribute to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. The presence of LRRK2 mutations exacerbate the pro-inflammatory state of the immune cells from the periphery. Infiltration of monocytes, T cells or cytokines through the blood brain barrier can induce the activation of microglia in the brain. The neuroinflammatory environment affects the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, contributing to the neurodegeneration.