FIG 3.
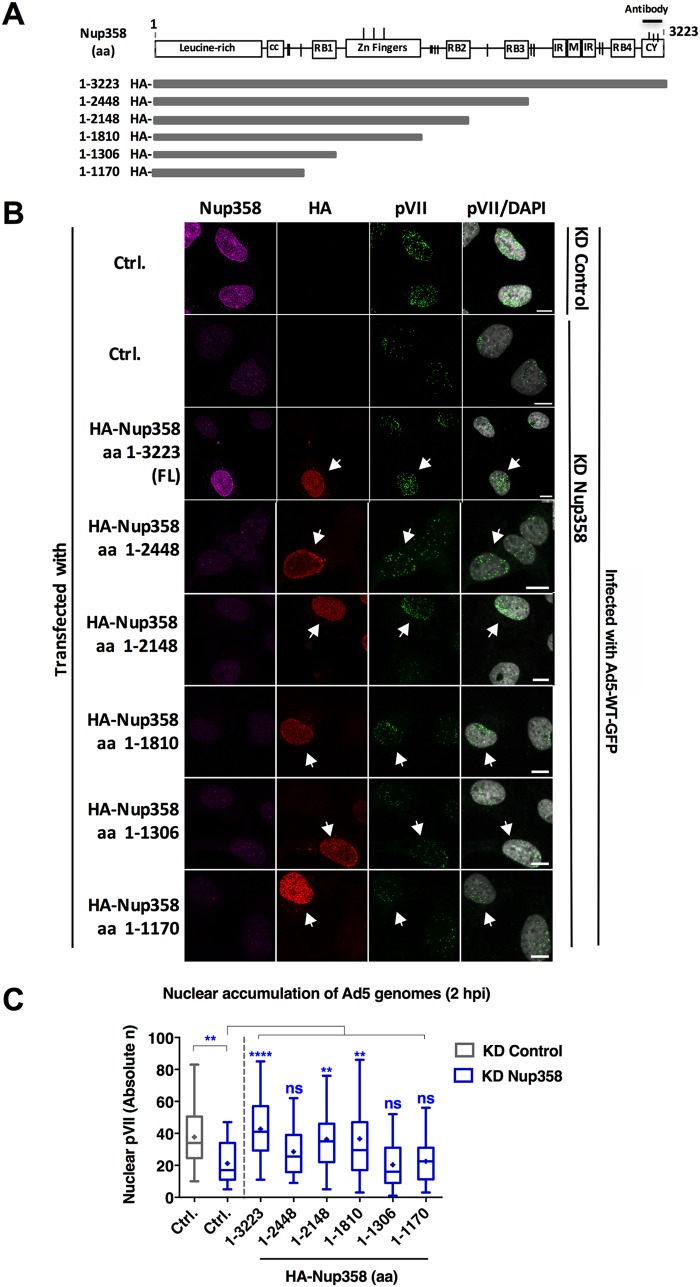
The N-terminal half of Nup358 is sufficient to promote efficient adenoviral genome import. (A) Schematic representation of the siRNA-resistant, HA-tagged constructs of Nup358 used in this assay (27). Numbers to the left of the horizontal bars representing the fragments indicate the corresponding amino acids (aa) present in each fragment. Domains of Nup358 are represented as boxes (cc, coiled coil domain; RB1, RB2, RB3, and RB4, Ran-binding domains; IR, internal repeat region; M, middle region; CY, cyclophilin-like domain), and vertical dashes show the positions of FG repeats. The N-terminal HA-epitope tag and the C-terminal antibody epitope in the CY of Nup358 are indicated. (B) U2OS cells were transfected with HA-tagged Nup358 fragments as indicated to the left, infected with Ad5-wt-GFP, fixed at 2 hpi, and processed for IF. Representative maximum projection confocal images of pVII accumulation in the nucleus of control cells (KD Control) or Nup358-depleted cells (KD Nup358), either control transfected (Ctrl.) or expressing full-length (FL) Nup358 or Nup358 truncation mutants as indicated, are shown. Antibodies used to detect endogenous Nup358 (magenta), the HA-epitope tag of transfected Nup358 (red), pVII (green), or pVII merged with the DAPI signal to mark the nucleus are indicated above each column. Note that the Nup358 antibody recognized the FL construct but not the truncation mutants. Arrows indicate cells expressing HA-Nup358 constructs. Bars, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of Ad5 genome import in control cells (gray) or KD Nup358 cells (blue) at t = 2 hpi represented as a box plot (n > 30 cells per condition). Results were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple-comparison post hoc test. Significance is indicated with respect to levels in control-transfected KD control cells (gray box).