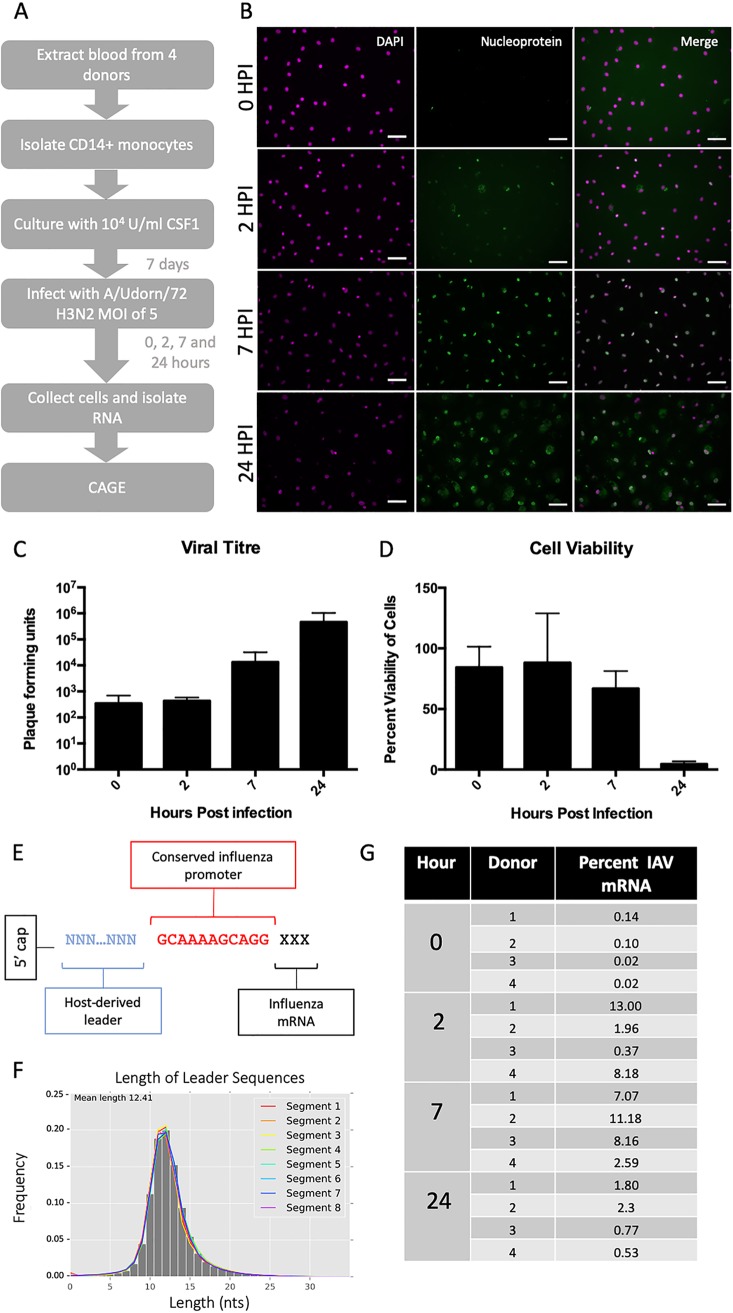
FIG 1.
Characterization of human monocyte-derived macrophages productively infected with IAV. (A) Experimental outline. Blood was taken from 4 human donors, with appropriate ethical approval. CD14+ monocytes were extracted using magnetic beads and cultured in CSF1 for 8 to 10 days. MDMs were infected with A/Udorn/72 (H3N2) virus at a multiplicity of infection of 5. At 4 time points (0, 2, 7, and 24 h after medium change) the cells were collected and RNA isolated. (B) Human MDMs were stained using antibodies specific for viral nucleoprotein to confirm infection at 0, 2, 7, and 24 h postinfection. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Viral titer was measured by plaque assay at 0, 2, 7, and 24 h postinfection (n = 3 independent experiments) and shown as PFU/ml supernatant. (D) Cell viability was measured using Cell Titer Glo at 0, 2, 7, and 24 h postinfection (n = 3 independent experiments). (E) Schematic showing the structure of the capped 5′ end of IAV mRNAs. (F) Length of leader sequences across segments. (G) Frequency, as percentage, of IAV promoter-containing CAGE tags in each IAV-infected sample.