FIG 3.
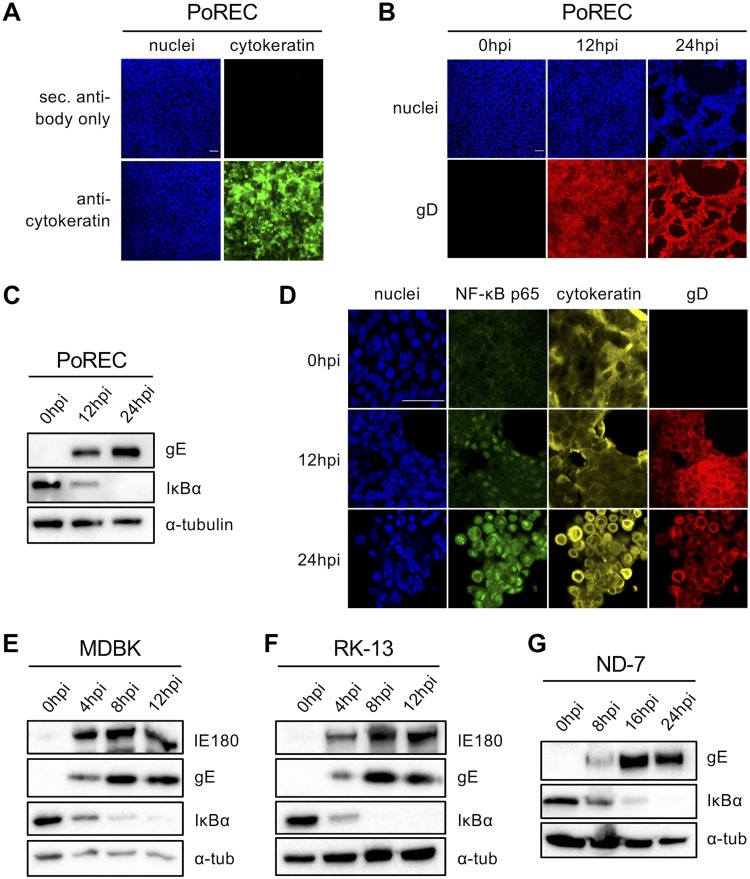
(A) Confocal microscopy of cytokeratin staining (and the corresponding secondary [sec.] antibody negative control) in tracheal porcine respiratory epithelial cells (PoRECs). Cytokeratin is shown in green, and nuclei are shown in blue. Bar, 50 μm. (B) Confocal microscopy of PRV gD expression in PoRECs infected with PRV Kaplan at 12 and 24 hpi (MOI, 10 PFU/cell; apical inoculation). PRV gD is shown in red, and nuclei are shown in blue. Bar, 50 μm. (C) Western blot analysis of IκBα in PRV Kaplan-infected PoRECs at 0, 12, and 24 hpi (MOI, 10 PFU/cell; apical inoculation). (D) Confocal microscopy of NF-κB p65 in PoRECs infected with PRV Kaplan at 0, 12, and 24 hpi (MOI, 10 PFU/cell; apical inoculation). NF-κB p65 is shown in green, cytokeratin is shown in yellow, gD is shown in red, and nuclei are shown in blue. Bar, 50 μm. The images in panels A to D are representative examples of the results obtained on PoRECs isolated from five different piglets. (E) Western blot analysis of IκBα in PRV Kaplan-infected bovine MDBK cells at 0, 4, 8, and 12 hpi (MOI, 10 PFU/cell). (F) Western blot analysis of IκBα in PRV Kaplan-infected rabbit kidney 13 (RK-13) cells at 0, 4, 8, and 12 hpi (MOI, 10 PFU/cell). (G) Western blot analysis of IκBα in PRV Kaplan-infected rat ND-7 cells at 0, 8, 16, and 24 hpi (MOI, 10 PFU/cell). The Western blots shown in panels E to G are representative examples from three independent repeats of the experiments.