Figure 4. Severity of IAV-induced lung dysfunction and cellular inflammation at 6 d.p.i. is dependent on expression of miR-155 in stromal cells.
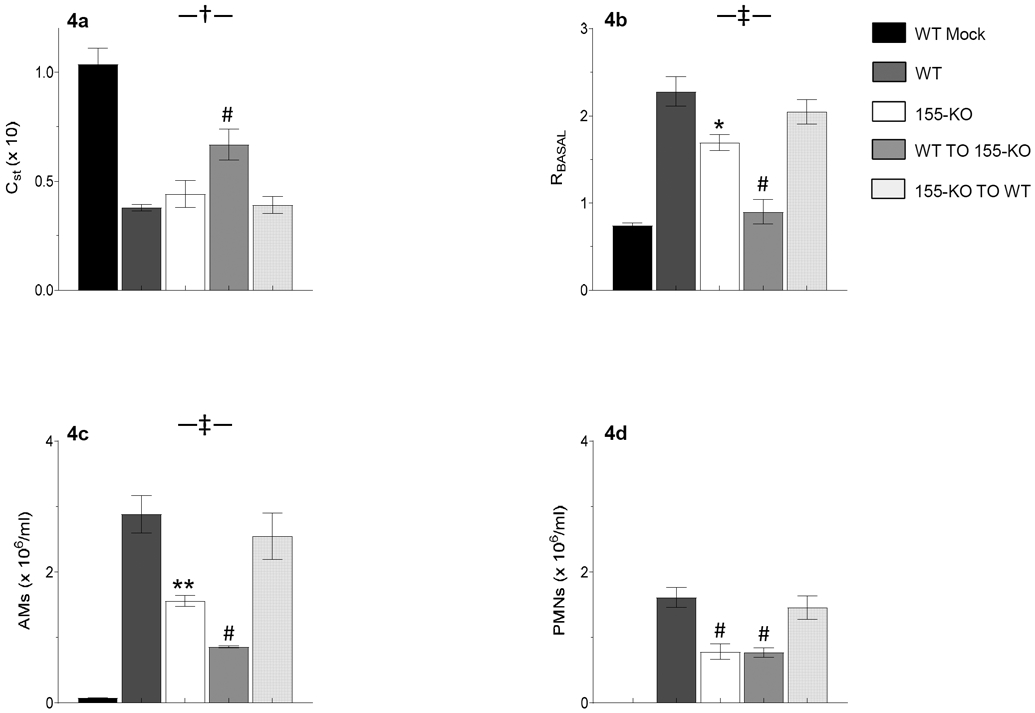
Effects of intranasal mock and IAV infection (with 10,000 pfu/mouse WSN virus) of wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice, C57BL/6-congenic global 155-KO mice, or mice that have undergone reciprocal bone marrow transfer on: (a) Static lung compliance (CST; ml/cmH2O, x 10); (b) Baseline total lung resistance (RBASAL; cmH2O.s/ml); (c) Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) alveolar macrophage (AM) counts (x 106/ml); and (d) BALF neutrophil (PMN) counts (x 106/ml). n>5 per group. No neutrophils were found in BALF from mock-infected WT mice. All data were analyzed by ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison post-test and are presented as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.005, #P<0.001, vs. WSN-infected WT mice. †P<0.05, ‡P<0.005, vs. WSN-infected 155-KO mice.
