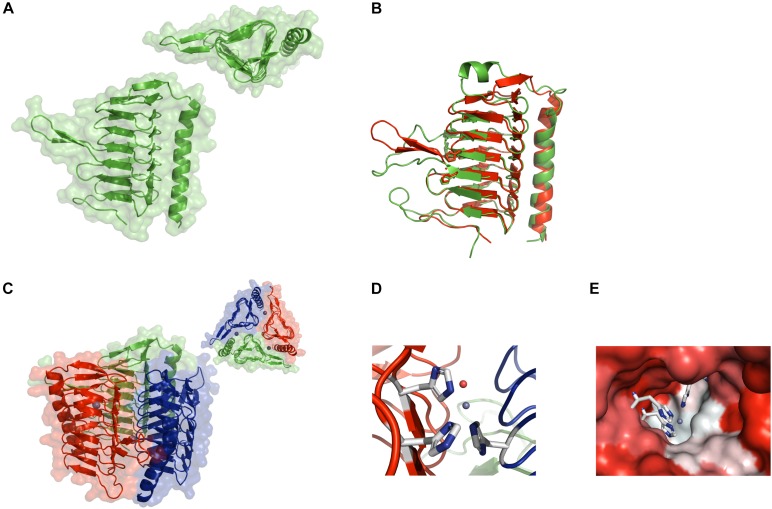
FIGURE 1.
Crystal structure of CA_D. (A) Ribbon structure of the CA_D monomer with the background showing the water-accessible surface. The inset shows a top view of the monomer depicting the triangular shape formed by the seven-turn, left-handed β-helix. (B) Structural overlay of the CA_D monomer (green) and the γ-CA Cam from Methanosarcina thermophila (red) (PDB ID 1qrg). (C) Ribbon structure of the CA_D trimer along with the water-accessible surface in the background. The inset contains a top view of the trimer. The three zinc ions are depicted as gray spheres. (D) The CA_D active center made up of three histidine residues (white-and-blue sticks) from two adjacent monomers. The zinc ion and a water molecule are depicted as gray and red spheres, respectively. (E) The active site cavity is colored according to hydrophobicity (red: hydrophilic, white: hydrophobic). The coordination residues are represented as sticks.