Figure 1.
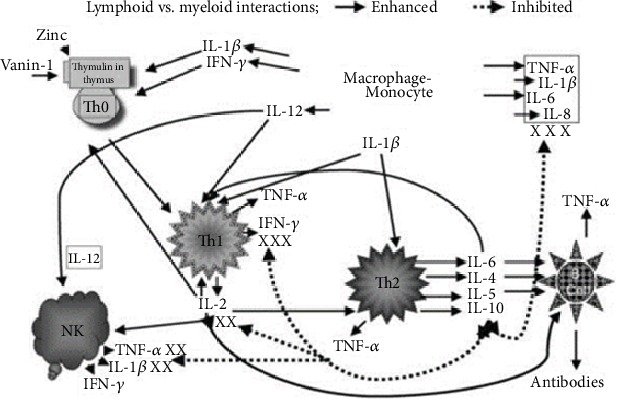
The landscape of zinc action on immune cells. Zinc is an essential component of thymulin, a thymic hormone involved in maturation and differentiation of T cells. The gene expression of IL-2 and IFN-γ (Th1 cytokines) is zinc dependent. IL-2 is involved in the activation of NK and T cytolytic cells. IL-12 is generated by stimulated macrophages-monocytes and is zinc dependent. IFN-γ and IL-12 together play a major role in the killing of parasites, viruses, and bacteria by macrophages-monocytes. Th2 cytokines are not affected by zinc deficiency except for IL-10 production, which is increased in the zinc-deficient elderly subjects. This is corrected by zinc supplementation. Increased IL-10 affects adversely Th1 and macrophage functions.
