Figure 7.
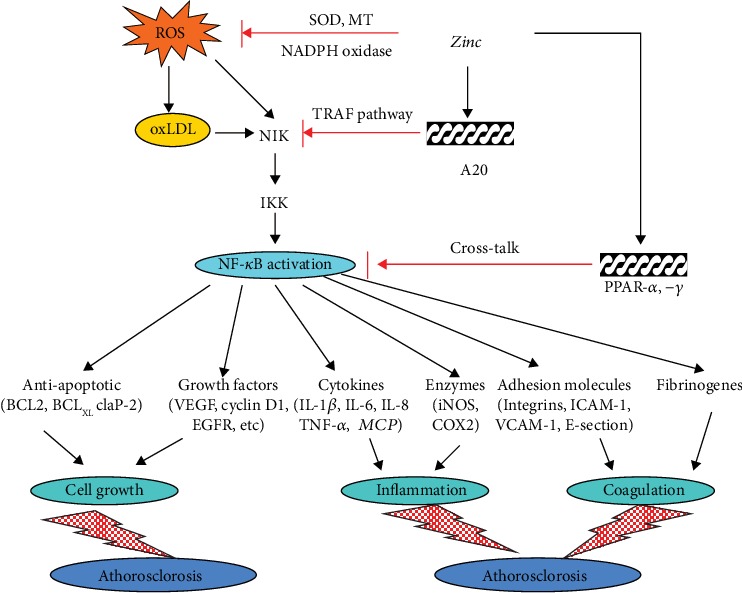
Our concept regarding the role of zinc as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) is known to activate NF-κB. Zinc decreases ROS generation. NADPH oxidase is inhibited by zinc and SOD, which is both a zinc and copper-containing enzyme that is upregulated. SOD is known to decrease oxidative stress. Metallothionein (MT) is induced by zinc and MT, which contains 26 moles of cysteine per mole of protein, decreasing OH burden. Zinc via A20 inhibits NF-κB activation, and this results in a decrease in generation of inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules. This figure also shows that zinc may have a preventive role in some cancers such as colon and prostate and in atherosclerosis inasmuch as chronic inflammation has been implicated in the development of these disorders [46, 47].
