Figure 1.
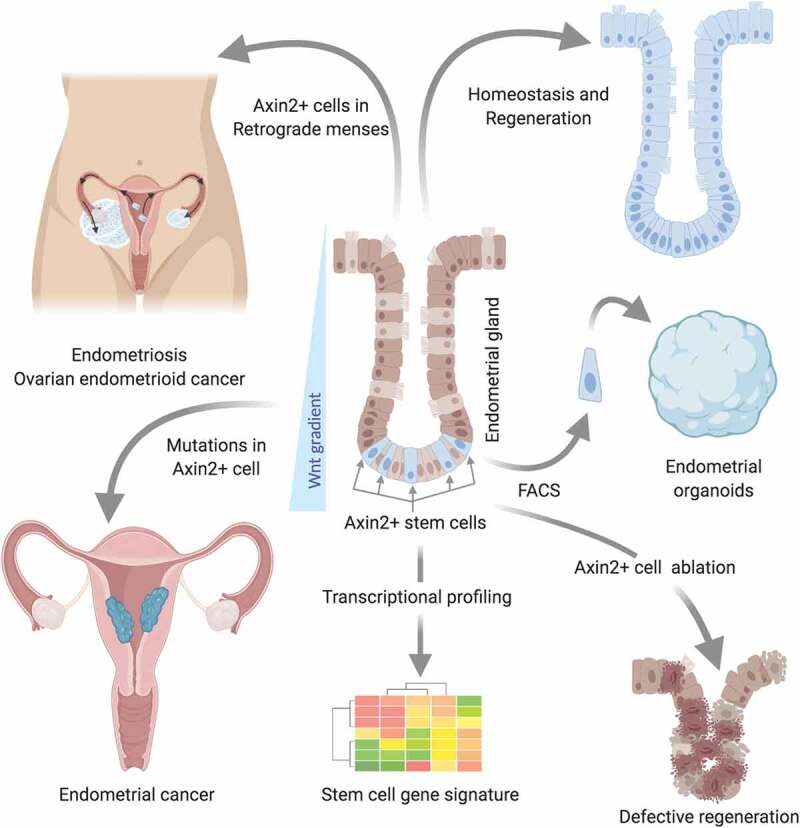
Identification of Axin2+ cells as stem cells of endometrial tissues and cancers via in vivo lineage tracing, ablation, and oncogenic transformation.
Axin2+ cells residing at gland bases are responsible for endometrial epithelial renewal during homeostasis and regeneration. Ablation of these cells compromises epithelial regeneration. These cells display a stem cell signature and have the exclusive capacity to form endometrial organoids. Oncogenic transformation of Axin2+ cells results in endometrial cancer development. When dislodged in retrograde menstruation these cells can seed in the peritoneal cavity and/or ovarian surface and possibly result in the growth of endometriotic tissue and ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma.
