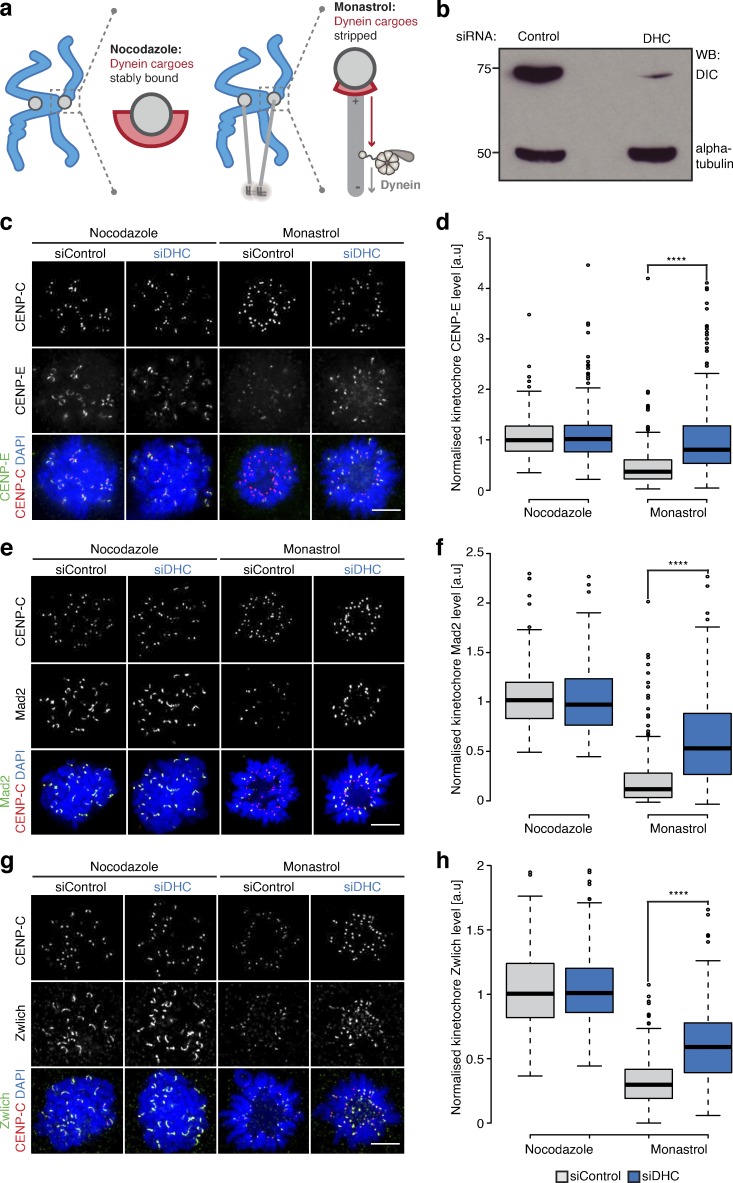
Figure 4.
Quantitative assay for dynein-mediated stripping. (a) Schematic outlining the dynein-stripping assay. Briefly, we compare cells arrested in nocodazole, where dynein cargoes are stably bound, and monastrol, where dynein can transport cargoes away from the syntelic (end-on attached) kinetochores toward the monopole. (b) Immunoblot of liquid-N2 extracts collected from HeLa-K cells treated with control or DHC siRNA. The membrane was probed with antibodies against DIC and α-tubulin. (c) Immunofluorescence microscopy images from the dynein-stripping assay for CENP-E. Cells were treated with control or DHC siRNA, arrested in nocodazole or monastrol, and stained with DAPI and antibodies against CENP-E and CENP-C. Scale bar, 5 µM. (d) Quantification of the kinetochore CENP-E intensity relative to CENP-C in the dynein-stripping assay as depicted in c. (e) Immunofluorescence microscopy images of the dynein-stripping assay for Mad2. Cells were treated with control or DHC siRNA, arrested with nocodazole or monastrol, and stained with DAPI and antibodies against Mad2 and CENP-C. Scale bar, 5 µM. (f) Quantification of the kinetochore-bound Mad2 intensity relative to CENP-C in the dynein-stripping assay depicted in e. (g) Immunofluorescence microscopy images of the dynein-stripping assay for Zwlich. Cells were treated with control or DHC siRNA, arrested with nocodazole or monastrol, and stained with DAPI and antibodies against Zwlich and CENP-C. Scale bar, 5 µM. (h) Quantification of the kinetochore Zwlich intensity relative to CENP-C in the dynein-stripping assay as depicted in g. In d, f, and h, boxes depict the median and first and third quartiles, and whiskers represent Q1 and Q3 ± 1.5× interquartile range. ****, P < 0.0001.