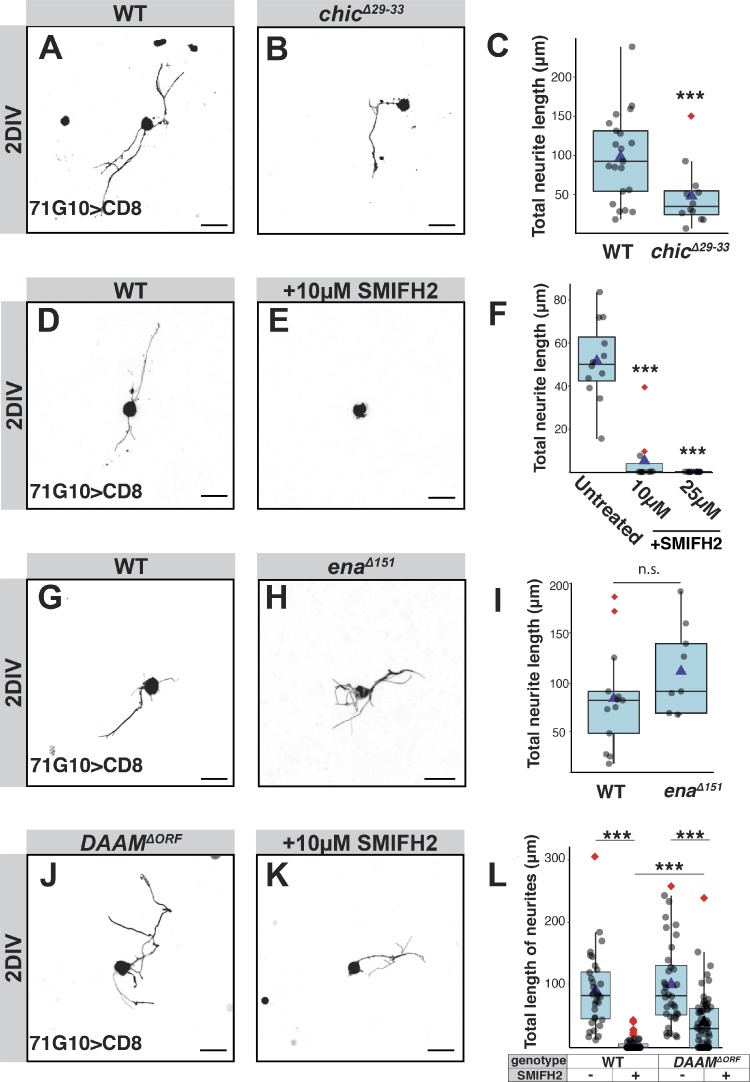
Figure 3.
Formins are required for axon sprouting, but deletion of DAAM initiates a formin-independent actin growth pathway. (A–L) The two left columns of panels in this figure depict confocal z-projections of single MB γ-neurons that were dissociated from third instar larval brains containing WT or mutant MARCM clones, as depicted, and grown for 2 DIV. Due to inherent variability in sprouting ability, controls were performed on the same day, in the same conditions as the experimental condition. Untreated WT neurons (A, n = 21; D, n = 15; G, n = 13), chicΔ29-33 (B, n = 12), WT neurons treated with 10 µM of the pan-formin inhibitor SMIFH2 (E, n = 11), enaΔ151 (H, n = 10), DAAMΔORF (J, n = 36), and DAAMΔORF treated with 10 µM SMIFH2 (K, n = 59). The right column of panels represents quantification of total neurite length of the MB γ-neurons shown in the left panels, except for F, which additionally also includes quantification of cells treated with 25 µM SMIFH2 (n = 13); ***, P = 0.006 (two-tailed t test; C); ***, P < 0.001 (Tukey's HSD; F); P = 0.2 (two-tailed t test; I); ***, P < 0.001 (two-tailed t test), also shows effect of SMIFH2 on each genotype (Cohen’s d test; L). In all box plots, boxes encompass the values in between the first and third quartiles; whiskers are ± 1.5 IQR; median (line), mean (blue triangle), and outliers (red diamond). Unless specifically marked otherwise, the significance level that is indicated above the box is in comparison to the WT. Gray is R71G10-Gal4–driven mCD8::GFP. Scale bars, 10 µm. n.s., not significant.