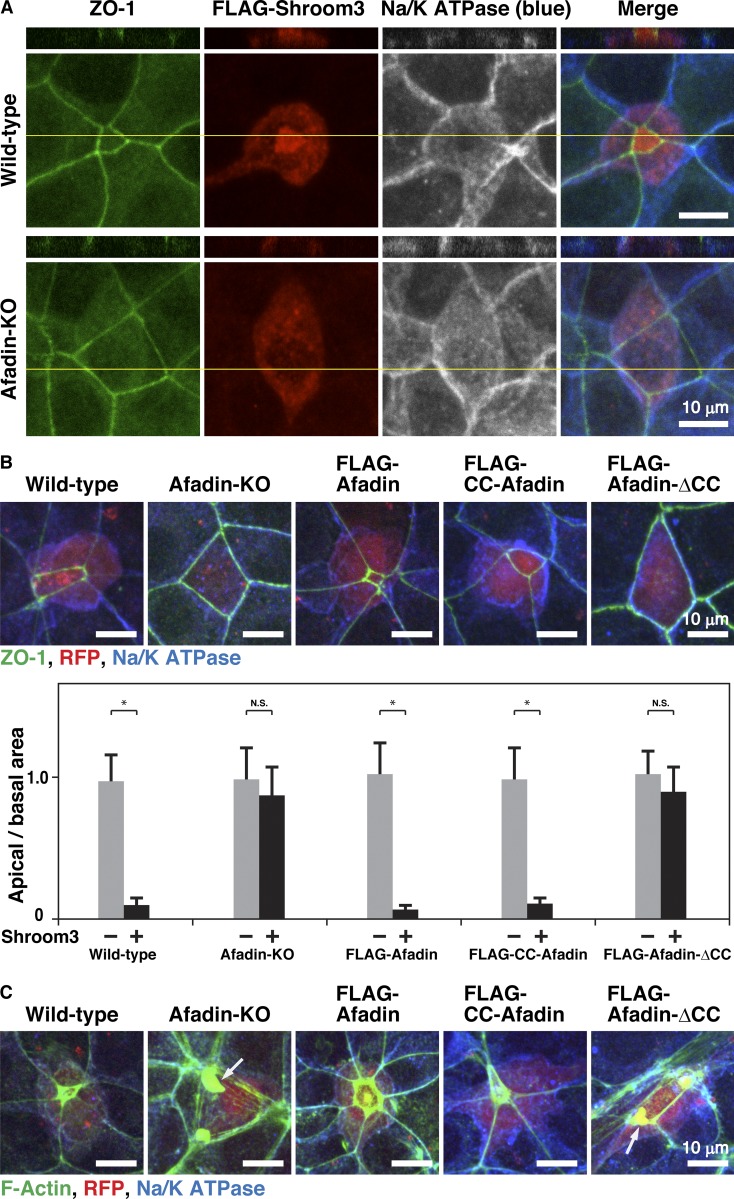
Figure 4.
Regulation of the proper actomyosin association with AJs by the binding of afadin to αE-catenin. (A) Requirement of afadin for the shroom3-induced apical constriction. 4 h after cell seeding, wild-type and afadin-KO cells were transfected with FLAG-shroom3 and incubated for 20 h. The cells were then fixed. The samples were stained with an anti–ZO-1 mAb (green), an anti-FLAG mAb (red), and an anti-Na/K ATPase pAb (blue), followed by immunofluorescence microscopic analysis. Projected xy views (lower panels) as well as z-sectional xz views (upper panels) are presented. Planes of orthogonal sections are indicated by yellow lines. (B) Requirement of the binding of afadin to αE-catenin for the shroom3-induced apical constriction. 4 h after cell seeding, wild-type, afadin-KO, FLAG-afadin, FLAG-CC-afadin, and FLAG-afadin-ΔCC cells were cotransfected with FLAG-shroom3 and RFP, and incubated for 20 h. The cells were then fixed. The samples were stained with the anti–ZO-1 mAb (green) and the anti-Na/K ATPase pAb (blue), followed by immunofluorescence microscopic analysis. Quantitative analysis is shown in the lower panel. The ratios of apical area and basal area are shown. Data are expressed as the means ± SD of three independent experiments (n = 10). *, P < 0.01 (two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test). N.S., not significant. (C) Requirement of the binding of afadin to αE-catenin for the proper actomyosin association with AJs during the shroom3-induced apical constriction. 4 h after cell seeding, wild-type, afadin-KO, FLAG-afadin, FLAG-CC-afadin, and FLAG-afadin-ΔCC cells were cotransfected with FLAG-shroom3 and RFP, and incubated for 20 h. The cells were then fixed. The samples were stained with phalloidin (green) and the anti-Na/K ATPase pAb (blue), followed by immunofluorescence microscopic analysis. Arrows indicate the F-actin signal in the cytoplasm.