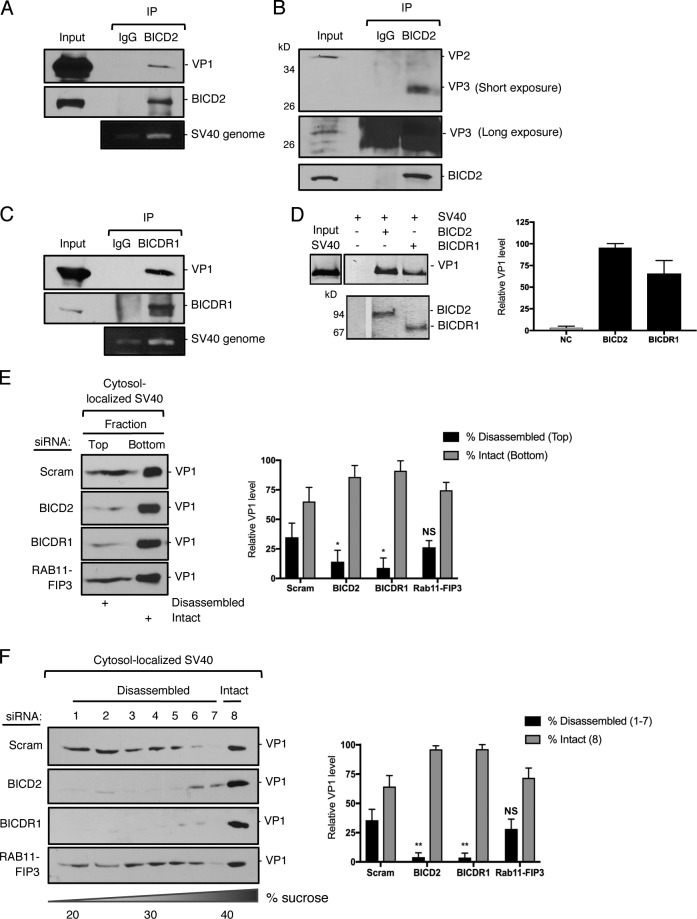
Figure 3.
BICD2 and BICDR1 bind to and promote SV40 disassembly in the cytosol during entry. (A) CV-1 cells were infected with SV40 (MOI ∼25) for 16 h. Endogenous BICD2 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from whole-cell extracts and the eluted samples subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting for VP1. DNA was isolated from the eluted sample and PCR performed to identify SV40 genomic DNA. (B) As in A, except immunoprecipitation by BICD2 was followed by immunoblotting for VP2/3. (C) As in A, except endogenous BICDR1 was immunoprecipitated. (D) In vitro binding assay of SV40 and full-length BICD2 and BICDR1. Purified His-tagged BICD2 and BICDR1 were separately linked to Nickel- Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) agarose resin. After incubation of these adaptors with SV40 (treated with DTT and EGTA), the immobilized proteins were eluted with imidazole and blotted with anti-VP1 antibody. The line indicates that lanes from the same immunoblot have been spliced together. (E) CV-1 cells were transfected with either a scrambled control siRNA, siRNA against BICD2, BICDR1 or RAB11-FIP3, and infected with SV40 (MOI∼5). At 16 hpi, the cytosolic fraction was isolated, layered on top of a 20% sucrose cushion, and centrifuged. Top and bottom fractions were collected and the presence of SV40 (VP1) assessed by immunoblotting. The levels of VP1 in the top fraction, corresponding to disassembled virus, and the bottom fraction, representing the intact virus, are quantified. (F) As in E, except the cytosolic fraction was layered over a discontinuous sucrose gradient (20–40% sucrose). Fractions were collected from the top of the gradient and the presence of SV40 (VP1) assessed by immunoblotting. The levels of VP1 in fractions 1–7, corresponding to disassembled virus, and fraction 8, representing the intact virus, are quantified. Values are averages of the means (n = 3) ± SD. A standard Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.005.