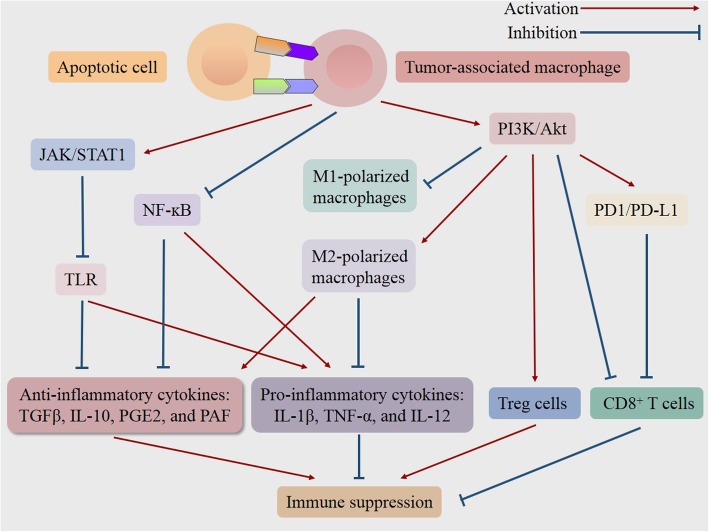
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of signaling pathways in the efferocytosis-induced immune suppression for tumor progression. The engulfment of apoptotic cells by tumor-associated macrophages triggers a series of signaling pathways, subsequently induces M2 polarization of macrophages while inhibiting M1 polarization, increases Treg cells while decreasing CD8+ T cells, and thereby resulting in the inflammation resolution and immune suppression, which may provide an environment for cancer to escape from immunological surveillance and promote tumor progression. NFκB = factor-κ-gene binding; JAK/STAT1 = Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription 1; PI3K/Akt = phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/protein-serine-threonine kinase; PD-1/PD-L1 = programmed death-ligand 1/programmed cell death protein 1; TLR = Toll-like receptor; IL = interleukin; TGFβ = transforming growth factor-beta; PGE2 = prostaglandin E2; PAF = platelet-activating factor; TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor-alpha; Treg cells = regulatory t cell