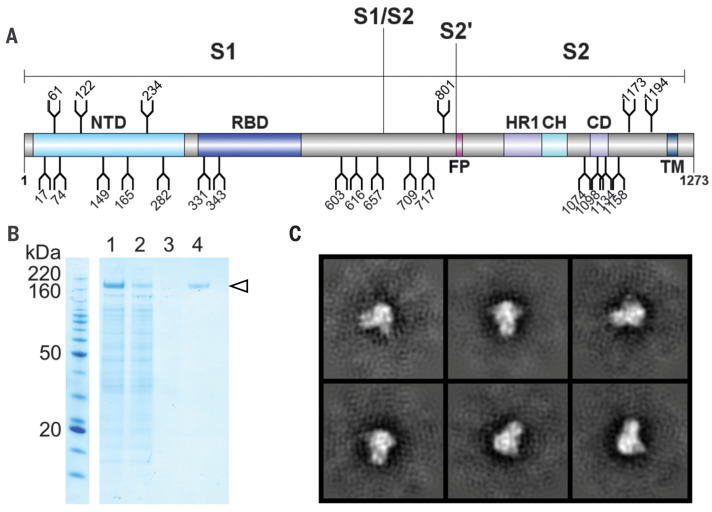
Fig. 1. Expression and validation of the SARS-CoV-2 S glycoprotein.
(A) Schematic representation of the SARS-CoV-2 S glycoprotein. The positions of N-linked glycosylation sequons (N-X-S/T, where X ≠ P) are shown as branches (N, Asn; X, any residue; S, Ser; T, Thr; P, Pro). Protein domains are illustrated: N-terminal domain (NTD), receptor binding domain (RBD), fusion peptide (FP), heptad repeat 1 (HR1), central helix (CH), connector domain (CD), and transmembrane domain (TM). (B) SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein (indicated by the arrowhead) expressed in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293F cells. Lane 1: filtered supernatant from transfected cells; lane 2: flow-through from StrepTactin resin; lane 3: wash from StrepTactin resin; lane 4: elution from StrepTactin resin. (C) Negative-stain EM 2D class averages of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein. 2D class averages of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein are shown, confirming that the protein adopts the trimeric prefusion conformation matching the material used to determine the structure (4).