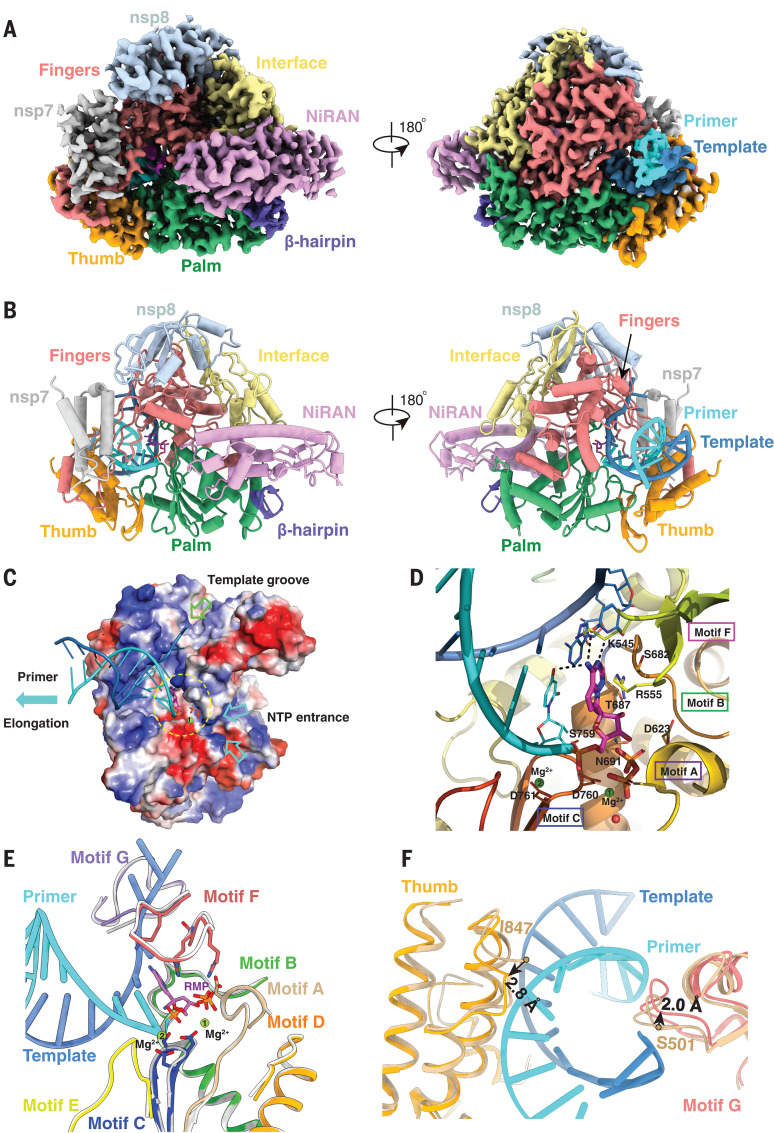
Fig. 3. Cryo-EM structure of the remdesivir- and RNA-bound RdRp complex.
(A and B) Two views of the cryo-EM map (A) and structure (B) of nsp12-nsp7-nsp8 in complex with template-primer RNA and remdesivir. (C) Surface view of the RdRp active site with the electrostatic potential from red (negative) to blue (positive). For clarity, residues 410 to 442 and 834 to 919 of nsp12 and nsp8 are excluded from the figure. The covalently bound remdesivir in the monophosphate form and the product, pyrophosphate, are shown. The active site is emphasized with a yellow dashed circle. The template groove, the entrance for nucleotide triphosphate (NTP), and the elongation direction are annotated with different-colored arrows. (D) Close-up view of the RdRp active site, showing the covalently bound RMP, pyrophosphate, and magnesium ions. Key residues and bases that interact with remdesivir are shown. (E and F) Superposition of the conserved RdRp motifs (A to G) of the RNA-bound complex with the apo structure (colored in gray), with a close-up view at the active site (E) and at the exit of the template and primer strand (F).