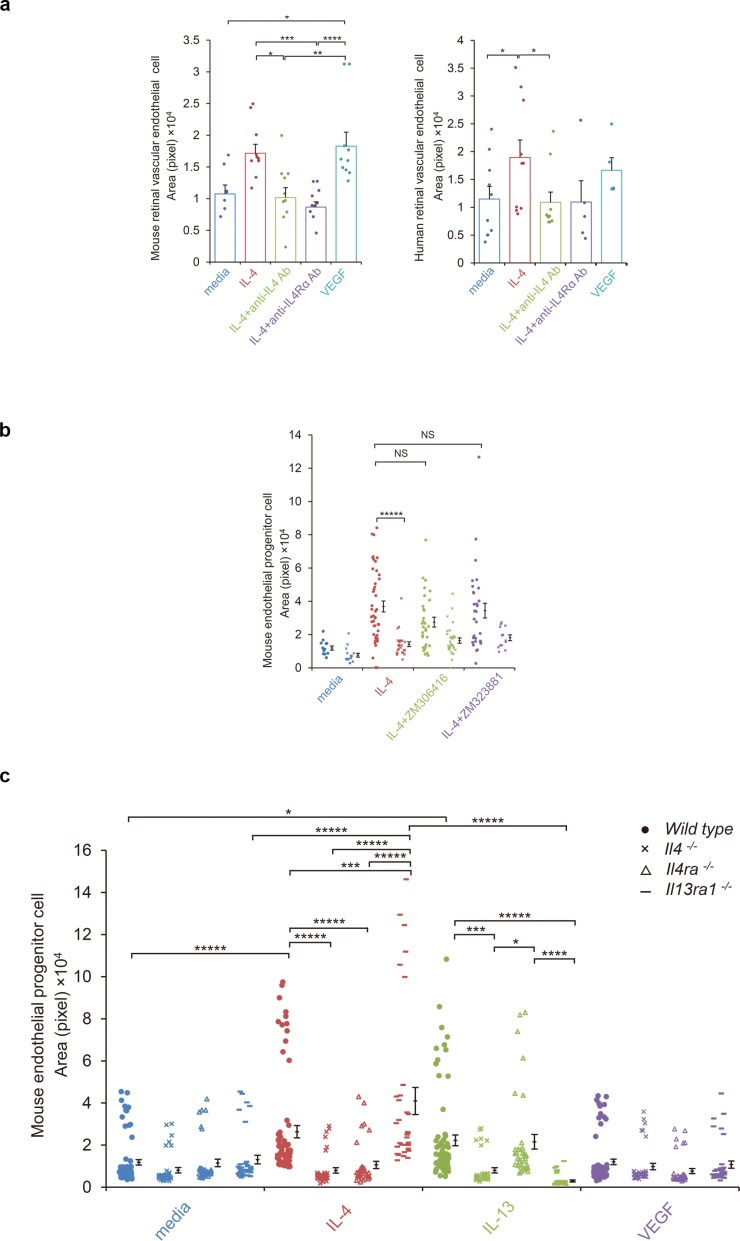
Figure 4. IL-4-induced tube formation in endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and retinal vascular endothelial cells.
(a) IL-4-induced tube formation of retinal vascular endothelial cells. Human and murine IL-4 exposure (10 ng/ml) significantly stimulated tube formation of human and murine retinal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro, respectively. Anti-IL-4 or IL-4Rα antibodies abolished the IL-4 induced-tube formation. VEGF exposure (10 ng/ml) also stimulated tube formation. (n = 7–10/group). (b) IL-4-induced tube formation in bone marrow-derived EPCs. IL-4 exposure (10 ng/ml) significantly stimulated tube formation of EPCs. The IL-4-induced tube formation was significantly reduced in EPCs from Il4ra-/- mice but was not affected by inhibition of VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase (ZM 306416) or VEGFR-2 (ZM 323881) (n = 13–45/group). (c) Requirements of IL-4 for tube formation response of EPCs. IL-4 (10 ng/ml) and IL-13 (10 ng/ml) induced tube formation of bone marrow-derived EPCs. These actions were abolished in the EPCs from Il4-/- bone marrow cells. EPCs from Il4ra-/- mice did not respond to IL-4, however they responded to IL-13 by tube formation. EPCs from Il13ra1-/- mice did not respond to IL-13 but responded to IL-4 by tube formation. (n = 35–72/group). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, ****p<0.001, *****p<0.0005. ANOVA with post hoc test and linear mixed-effects regression analysis.