Figure 5. Proposed protective effects of apolipoprotein M in heart failure.
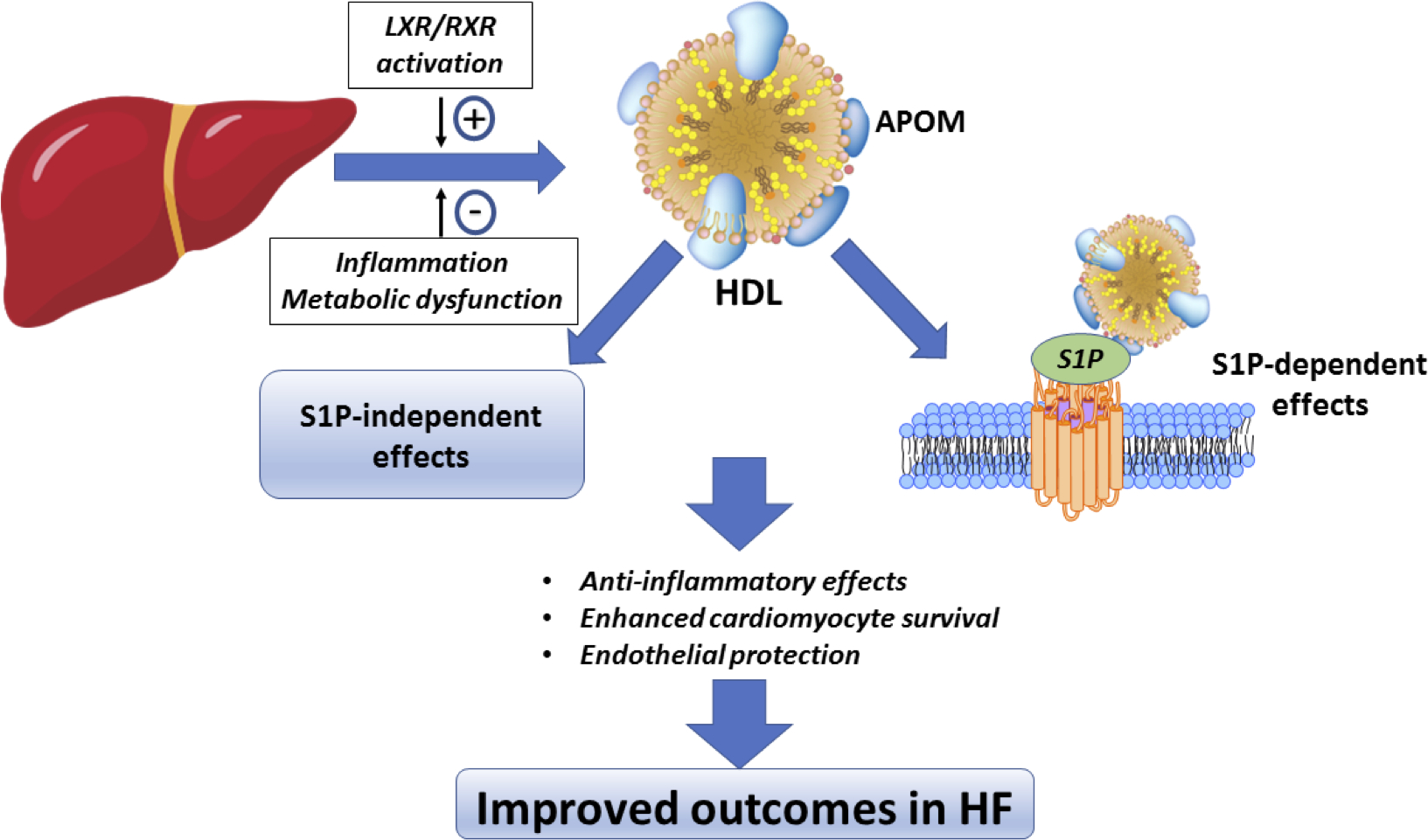
APOM is associated with HDL and binds S1P. S1P signaling enhances cardiomyocyte survival, activates endothelial protective pathways, and is anti-inflammatory. The culmination of these effects may result in improved survival in heart failure. However, whether the relationship between APOM and outcomes is causal remains to be determined.
